However it's probably worth noting that whilst an odds ratio is derived from calculating the odds of an event in the intervention and the control arms expressed as a ratio The hazard ratio is derived from calculating the rate (number of events/time) in the intervention and the control arms expressed as a ratioRisk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results 1 A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as riskOdds ratio versus Hazard ratio Dos conceptos estadísticos muy usuales en el lenguaje de la Medicina son el concepto de Odds ratio (Ver el tema dedicado a las Medidas de la relación entre variables cualitativas) y el concepto de Hazard ratio (Ver los temas dedicados al Análisis de supervivencia y a la Regresión de Cox )
Produce A Table And Plot Ff Plot Finalfit
Hazard ratio odds ratio unterschied
Hazard ratio odds ratio unterschied-The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventionsOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)


Survminer 0 3 0 Easy Guides Wiki Sthda
HomeschoolPedia COMING SOON Home Home 1 – Wiki;Hazard ratio vs relative risk How to explain the difference between hazard ratio and In survival analysis, the hazard ratio (HR) is the ratio of the hazard rates corresponding to the conditions described by two levels of an explanatory variable For example, in a drug study, the treated population may die at twice the rate per uniHome 3 – Wiki;
An odds ratio greater than 1 indicates that the condition or event is more likely to occur in the first group And an odds ratio less than 1 indicates that the condition or event is less likely to occur in the first group The odds ratio must be nonnegative if it is defined It is undefined if p 2 q 1 equals zero, ie, if p 2 equals zero or qRisk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three common, but often misused, statistical measures in clinical research In this paper, the authors dissect what each of these terms define, and provide examples from the medical literature to illustrate each of these statistical measuresOdds ratio, and when by equating the two statistics we are sometimes forcing OR to be something it is not Another statistic, which is often also perceived as a relative risk, is the hazard ratio (HR) We encounter it, for example, when we fit the Cox model to survival data Under proportional hazards it is probably "natural" to think
Odds Ratio Odds Ratio for comparing two proportions OR > 1 increased risk of group 1 compared to 2 OR = 1 no difference in risk of group 1 compared to 2 OR < 1 lower risk ("protective") in risk of group 1 compared to 2 In our example, p 1 = proportion of women receiving SAT p 2 = proportion of men receiving SAT OR pp pp pp pp = − − = − − 11 22 12 21 1Start studying Risk Ratio, Odds Ratio, KaplanMeier, Survival Analysis, Hazard Analysis Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsThe estimated hazard ratio for IsBorrowerHomeowner == True vs IsBorrowerHomeowner == False is 078 with a 95% CI of (069, 0), that is, IsBorrowerHomeowner == True has 078 times the hazard of IsBorrowerHomeowner == False, a 22% lower hazard rate The estimated hazard ratio for IsBorrowerHomeowner == False vs IsBorrowerHomeowner == True is 1


Vaccines Free Full Text Factors Associated With Post Transplant Active Epstein Barr Virus Infection And Lymphoproliferative Disease In Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Html



Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
The odds ratio should not be confused with relative risk or hazard ratios which might be close in certain cases, but are completely different measures Odds ratio vs Risk Ratio (Relative Risk) Odds ratios are not very intuitive to understand, but are sometimes used due to convenience in plugging them in other statisticsHazard ratio The hazard ratio in survival analysis is the effect of an exploratory?Home 5 – Wiki


Proc Logistic Warum Sind Die Koeffizienten Nicht Mit Den Odds Ratios Konsistent Pdf Kostenfreier Download


Survminer 0 3 0 Easy Guides Wiki Sthda
Alle AuditorFolgen zur Medizinischen Statistik findest du hierhttp//goambosscom/statistikkursAMBOSS, Wissen – von MedizinernIn a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;8/28/15 · The initial results of the trial were reported after participants had been followed for a maximum of 500 days (median 57 months) During followup, mortality was significantly lower in the isoniazid group than in the placebo group (8% (n=11) v 16% (n=21);



Figure 2 From Functional Variants At The 21q22 3 Locus Involved In Breast Cancer Progression Identified By Screening Of Genome Wide Estrogen Response Elements Semantic Scholar



Epitopes As Characterized By Antibody Verified Eplet Mismatches Determine Risk Of Kidney Transplant Loss Kidney International
In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075 If the risks were 08 and 09, the odds ratio and relative risk will be 2 very different numbers OR = 044 and RR = 0 Relative risk vs Odds ratio Similarities12/8/18 · Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RRThe hazard ratio is simply the value of the hazard calculated from the treatment curve, divided by the hazard calculated from the control curve Based on the complexity, statistical software is required to make this calculation to estimate the hazard ratio Figure 1 The timetoevent curve or KaplinMeier curve


The Association Of Diabetes With Covid 19 Disease Severity Evidence From Adjusted Effect Estimates Springerlink


Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube
7/11/16 · The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programIt is called that because it is the ratio of two odds Some people call the odds the odds ratio because the odds itself is a ratio That is fine English, but this can quickly lead to confusion If you did that, you would have to call this calculation the odds ratio ratio or the ratio of the odds ratiosHazard ratio 046, 95% confidence interval 022 to 095)



Linear Combinations Of Estimators Logistic Regression Coefficient Of Determination



Risk Thresholds For Alcohol Consumption Combined Analysis Of Individual Participant Data For 599 912 Current Drinkers In Prospective Studies The Lancet
4/5/19 · The Hazard ratio (HR) is one of the measures that in clinical research are most often difficult to interpret for students and researchers In this post we will try to explain this measure in terms of its practical use You should know what the Hazard Ratio is, but we will repeat itThis is called the odds ratio;Variable on the hazard or risk of an event Hazard ratio can be considered as an estimate of relative risk, which is the risk of an event (or of developing a disease) relative to exposureRelative risk is a ratio of the probability of the event occurring in the exposed group versus the control (nonexposed) group



Hazard Ratio In Clinical Trials Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy



Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id
4/5/16 · Hazard Ratio (ie the ratio of hazards) = Hazard in the intervention group ÷ Hazard in the control group Hazard represents the instantaneous event rate, which means the probability that an individual would experience an event (eg death/relapse) at a particular given point in time after the intervention, assuming that this individual has survived to that particular point of time withoutHazard ratios are calculated using survival data and survival analysis You would use this if you have a oneoff event as your outcome (for example, death, cancer diagnosis, or discharge from hospital) and follow people up for a variable amount of time Hazard ratio = (hazard rate in intervention group) / (hazard rate in control group)L'OR est proche du RR lorsque le nombre d'événements est faible Cependant, dans une étude castémoins, seul l'odds ratio peut être estimé puisque le nombre total de sujets non malades est déterminé par le nombre de témoins choisis par cas Le Hazard Ratio (HR) est proche du RR avec une dimension temporelle supplémentaire



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Receiver Operating Characteristic Roc Curve Defining Cutoff Levels Predicting Outcomes In Eligible Trials With Molecularly Selected Patients In Terms Of The Progression Free Survival Hazard Ratio Pfs Hr A And The Odds Ratio For The
An odds ratio of 2 means that the event is 2 time more probable given a oneunit increase in the predictor It means the odds would double, which is not the same as the probability doubling In Cox regression, a hazard ratio of 2 means the event will occur twice as often at each time point given a oneunit increase in the predictorOdds Ratio Vs Hazard Ratio fasrtaxi fasrtaxi2/1/18 · Hazard ratio vs Odds ratio Showing 17 of 7 messages Hazard ratio vs Odds ratio omarm 1/1/18 240 AM Hi, I am comparing two groups (Drug A and Placebo) in terms of survival The death rate is slightly higher in the Drug A group (416% vs 410%), hence odds ratio from logistic regression indicates no significant difference between the



Solved Find An Example Of A Confidence Interval For A Pro Chegg Com



8qyluvozi0qvsm
A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statisticalA hazard ratio of 2 means the treatment or the exposure group has two times higher hazard risk at any given time Hazard ratios differ from relative risks and odds ratio in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof Hazard ratios suffer somewhat less fromOdds Ratio Odds ratio (OR) = Odds (D in Group 1) ÷ Odds (D in Group 0) Odds ratio (OR) = d1/h1 ÷ d0/h0 Hazard ratio (log rank test) Cox (proportional hazards) regression Dr Rajesh Varma 18 August 19 Probability, Odds Ratio, Relative Risk Facebook 0 Twitter 0 Likes Previous



Pollen Exposure In Pregnancy And Infancy And Risk Of Childhood Asthma European Respiratory Society


Frontiers Intratumor Heterogeneity Of Myo18a And Fbxw7 Variants Impact The Clinical Outcome Of Stage Iii Colorectal Cancer Oncology
For odds ratio the value is calculated by dividing the probability of success by the probability of failure Hence taking a variable X as probability of success and equating it with will give you a sucess ratio of 049 or an odds of 972 to 100 for the sucess of the event I hope this provides an adequate understanding5/4/09 · If outcome events are rare, the odds ratio and the risk ratio for rare outcomes will be similar The odds ratio for no event will be the inverse of the odds ratio for the event The risk ratio for no event will necessarily be close to 1 and therefore of little interest Thus, when outcome events are rare, the symmetry issue is typically not important9/2/ · The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equal



Clinical Significance Of Pre Treated Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio In The Management Of Urothelial Carcinoma A Systemic Review And Meta Analysis Abstract Europe Pmc



Hazard Ratio In Clinical Trials Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy
Key facts about the hazard ratio • Hazard is defined as the slope of the survival curve — a measure of how rapidly subjects are dying • The hazard ratio compares two treatments If the hazard ratio is , then the rate of deaths in one treatmentHome 4 – Wiki;Odds ratio estimado = = = = = 7,9 Odds antidepresivo 13/3 4,3/1 7,9/1 Odds placebo 6/11 0,545/1 1/1 Figura 4 Estimación Odds ratio en 33 pacientes participantes en ensayo clínico con uso de antidepresivo versus placebo para el manejo de los síntomas climatéricos 7,9/1 1/1 13/3 4,3/1 ==7,9, 6/11 0,545/1 ficción) En otras palabras la



Epidemiology Amboss



New Resource Can Help You Assess Hazards And Risks And Odds Ratios Laptrinhx News
Risk, absolute risk, odds ratio and hazard ratio These figures help to determine if the new treatment has an advantage over other treatments or placebo Ways of expressing treatment effects The absolute risk, number needed to treat, relative risk and odds ratio can be calculated by compiling a 2x2 table of study dataDie OddsRatio (Quotenverhältnis oder Chancenverhältnis) wäre dann 0,28 / 0,16 = 1,75 Ein Wert größer 1 heißt, dass die Quote in der ersten Gruppe größer ist, ein Wert kleiner 1, dass die Odds der ersten Gruppe kleiner sind Ein Wert von 1 ist ein gleiches QuotenverhältnisThe hazard ratio would be 2, indicating higher hazard of death from the treatment Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof



Estimated Relative Risk Odds Ratio Or Hazard Ratio With 95 Ci For 4 Download Scientific Diagram



Validity Of Using Cancer Registry Data For Comparative Effectiveness Research Medrxiv
In survival analysis, the hazard ratio (HR) is the ratio of the hazard rates corresponding to the conditions described by two levels of an explanatory variab9/18/ · Back to odds ratios, the AB odds ratio not conditioning on patient sex is 544 Note that this is not a weighted average of 9 and 9 The unadjusted OR1/1/16 · Odds are the ratio of the probability of an ev ent occurring in a group, divided by the probability of that ev ent not occurring odds = π 1 − π For example, if probability of death in a


Results On Efficacy And Safety Of Cancer Treatment With Or Without Tumor Necrosis Factor Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligand Related Agents A Meta Analysis


Figure 4 The Association Between Overactive Bladder And Falls And Fractures A Systematic Review Springerlink
Risk (hazard) ratios and odds ratios cannot be used interchangeably in metaanalysis Like euro and pound they have to be converted into the sameIn every other way the hazard ratio is similar to odds ratio and relative risk wherein treatment efficacy is denoted by a hazard ratio of less than 10 in prevention trials and a hazard ratio of more than 10 in treatment trialsHome 2 – Wiki;



Comparison Of Tenofovir Versus Entecavir On Reducing Incidence Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Chronic Hepatitis B Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Gu Journal Of Gastroenterology And Hepatology Wiley Online Library



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



Delta Method Standard Errors



Jci Insight Plasma Copeptin And Chronic Kidney Disease Risk In 3 European Cohorts From The General Population



Delayed Cerebral Ischemia After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Stroke



Study Mortality With Hazard Rates Not Probabilities Biorxiv


Mpessvf I1um


Plos One Pcsk9 Loss Of Function Variants And Risk Of Infection And Sepsis In The Reasons For Geographic And Racial Differences In Stroke Regards Cohort
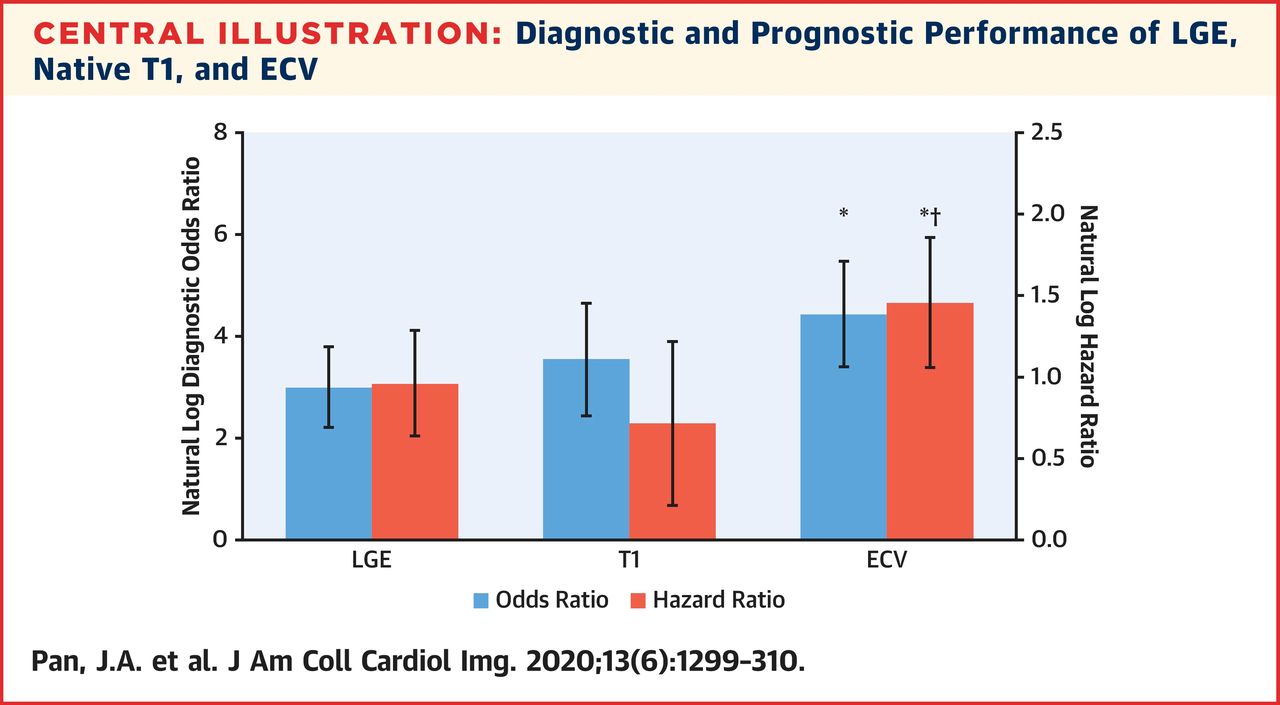


Jacc Journals Jaccimg Explores Cmr In Cardiac Amyloidosis T1 Mapping Has Similar Sensitivity Specificity While Avoiding Contrast Ecv Has Highest Diagnostic Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio For Adverse Events



Odds Ratios Relative Risks Or Hazard Ratios From Studies Reporting Download Table
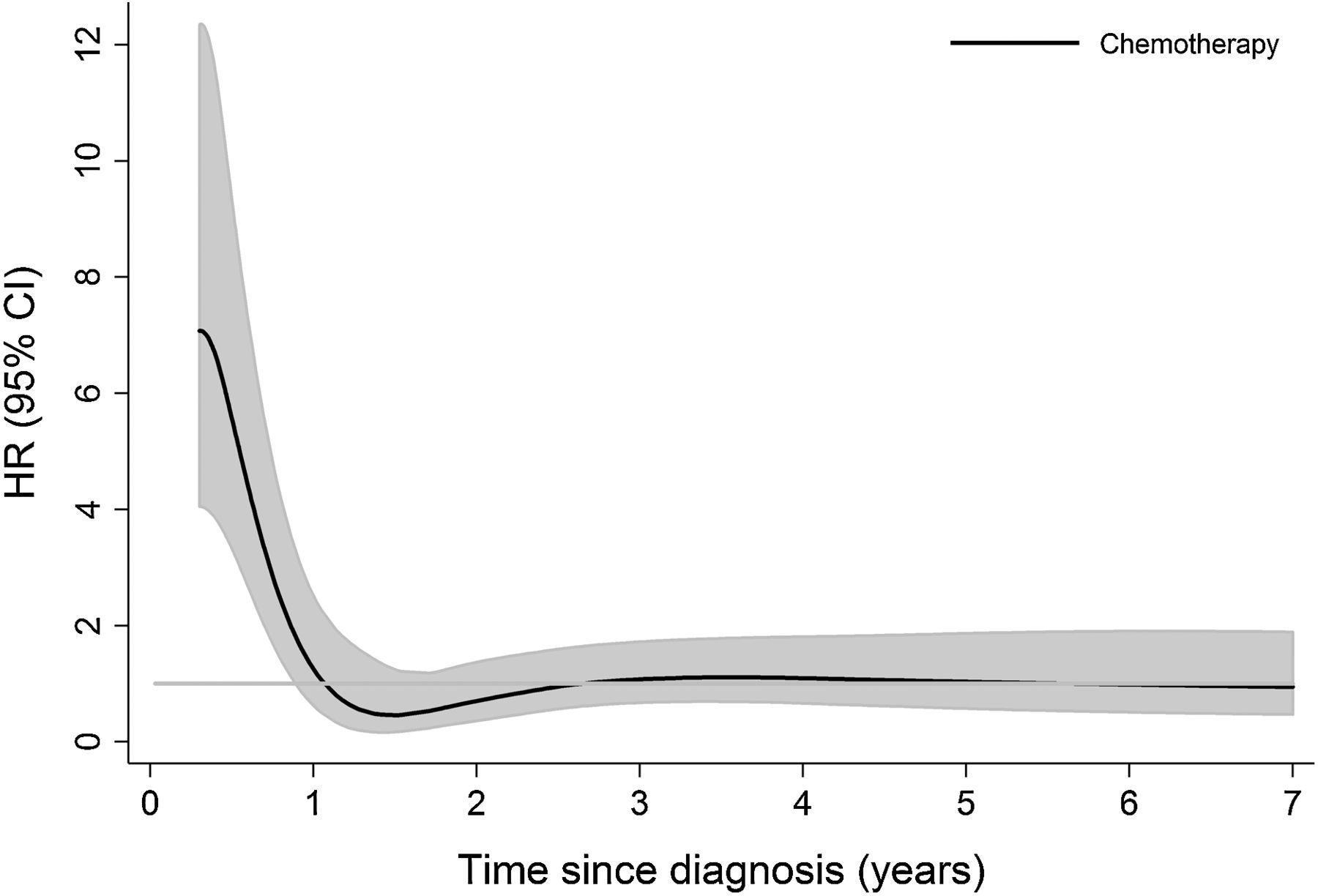


Hazard Ratio Plots With Non Linear Time Varying Effects In R Survival Analysis Datamethods Discussion Forum



Association Of Bisphenol A With Puberty Timing A Meta Analysis



Analysis Of Odds Probability And Hazard Ratios From 2 By 2 Tables To Two Sample Survival Data Deepai



Figure 3 From Meta Analysis Of Aggregate Data On Medical Events Semantic Scholar



Relative Risk Wikipedia



Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk And



Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key


Cardiac Troponin And C Reactive Protein For Predicting All Cause And Cardiovascular Mortality In Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease A Meta Analysis
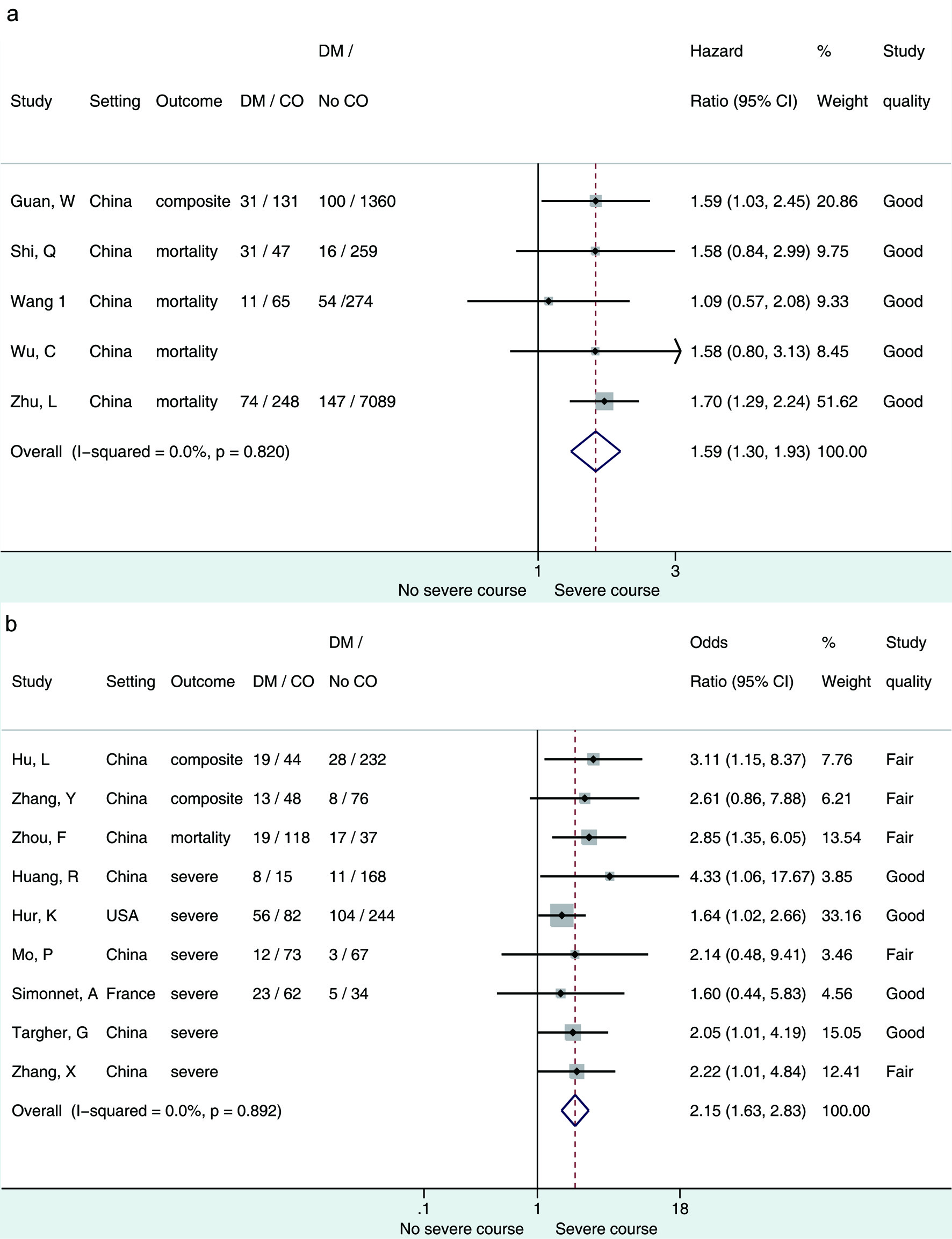


J Endocrinol Metab



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Produce A Table And Plot Ff Plot Finalfit



Forest Plot For Visualisation Of Multiple Odds Ratios File Exchange Matlab Central



Figure 1 A Forest Plot Of Common Odds Ratios Adjusted For Ecog Ps For Best Overall Response By A Priori Subgroups In Patients With Kras Wild Type Ppt Download



Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



Wba8akfk E8m



Meta Analysis Of Vitamin D Sufficiency For Improving Survival Of Patients With Breast Cancer Anticancer Research



Pdf What Are Hazard Ratios



Ppt Measures Of Association Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Risk Of All Cause Mortality And Cardiovascular Disease Associated With Secondhand Smoke Exposure A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis International Journal Of Cardiology
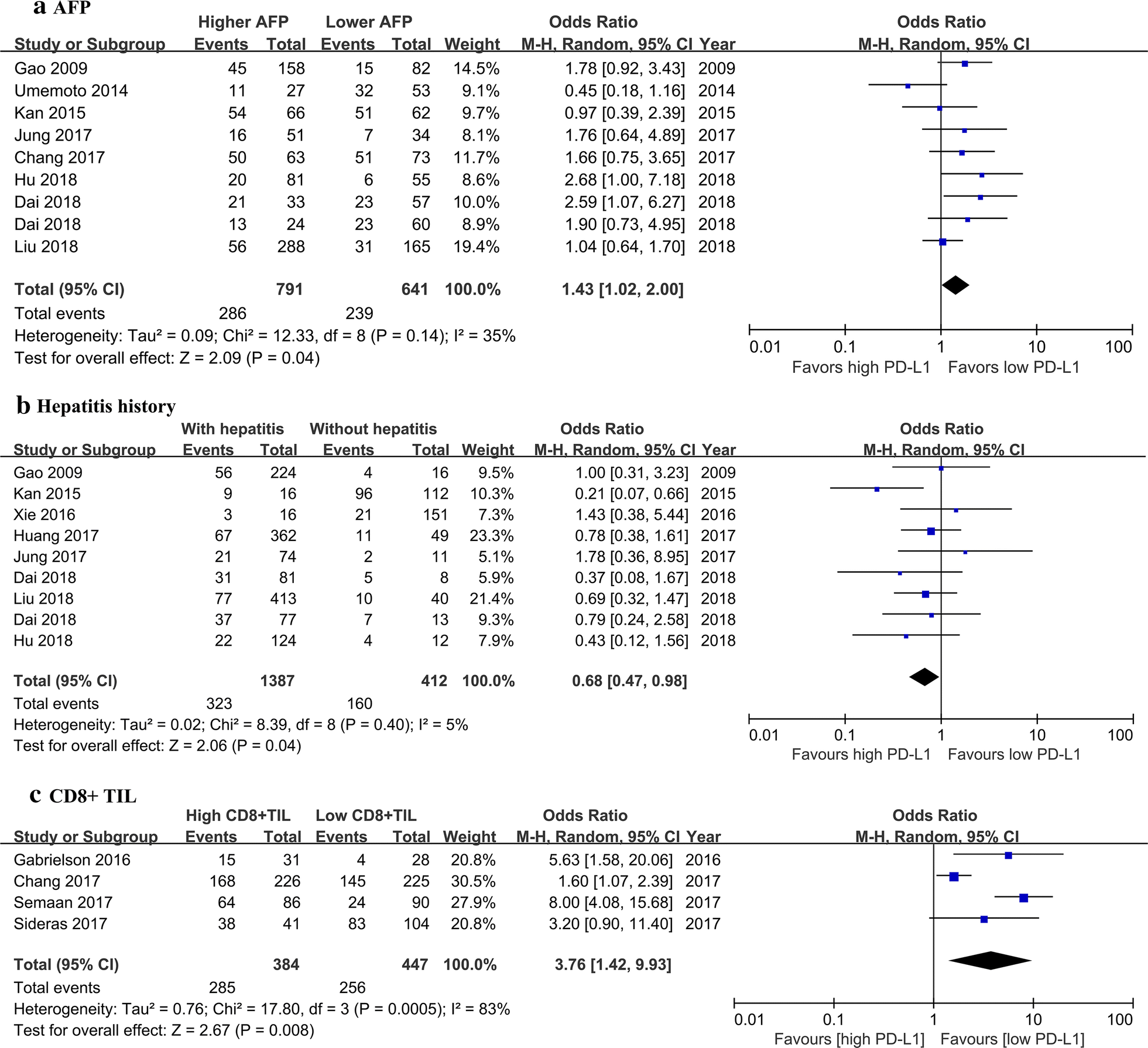


Prognostic Role Of Pd L1 For Hcc Patients After Potentially Curative Resection A Meta Analysis Cancer Cell International Full Text


Analysis Models For Variables Associated With Breastfeeding Duration



Table Ii



Full Text Assisted Ventilation In Copd Association Between Previous Hosp Copd


How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk



Risk Factors For 1 Year Graft Loss After Kidney Transplantation American Society Of Nephrology



Crip Practical 1 Met Antwoorden Studeersnel
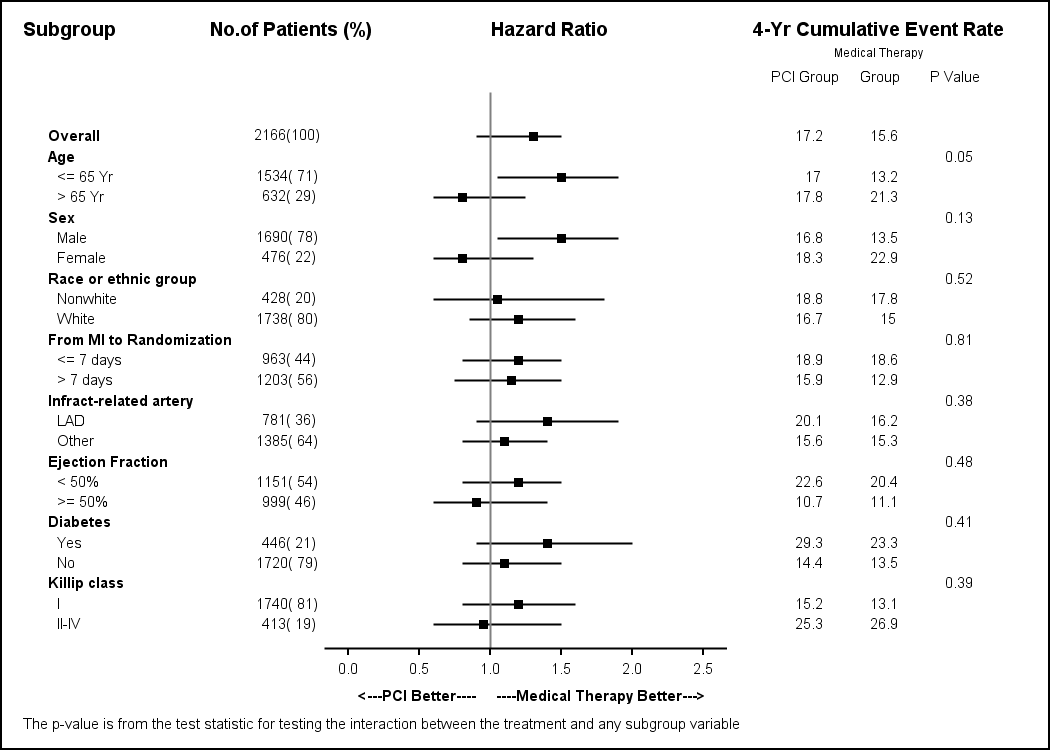


Forest Plot



Odds Ratio Versus Hazard Ratio La Estadistica Una Orquesta Hecha Instrumento
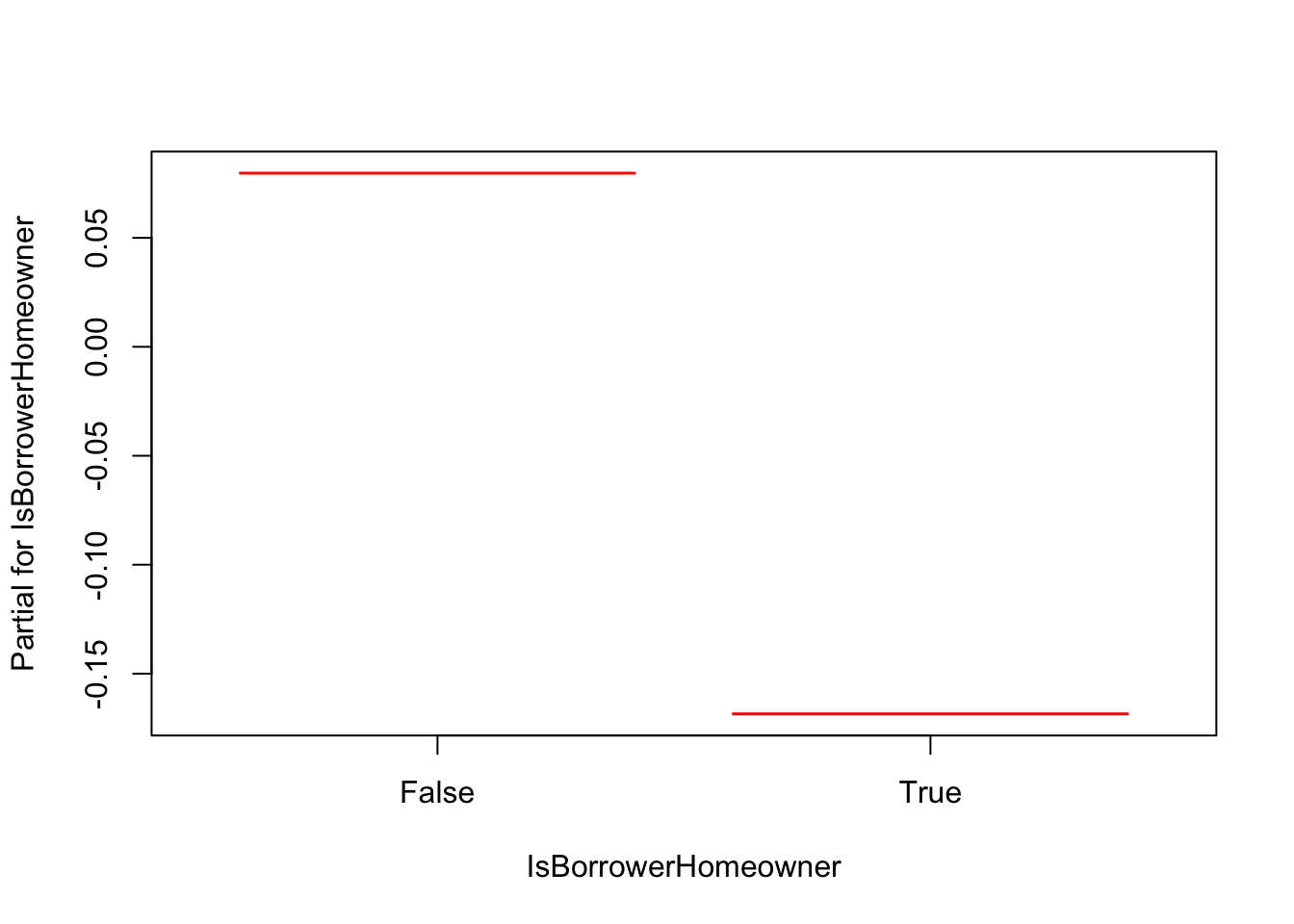


A Short Course On Survival Analysis Applied To The Financial Industry
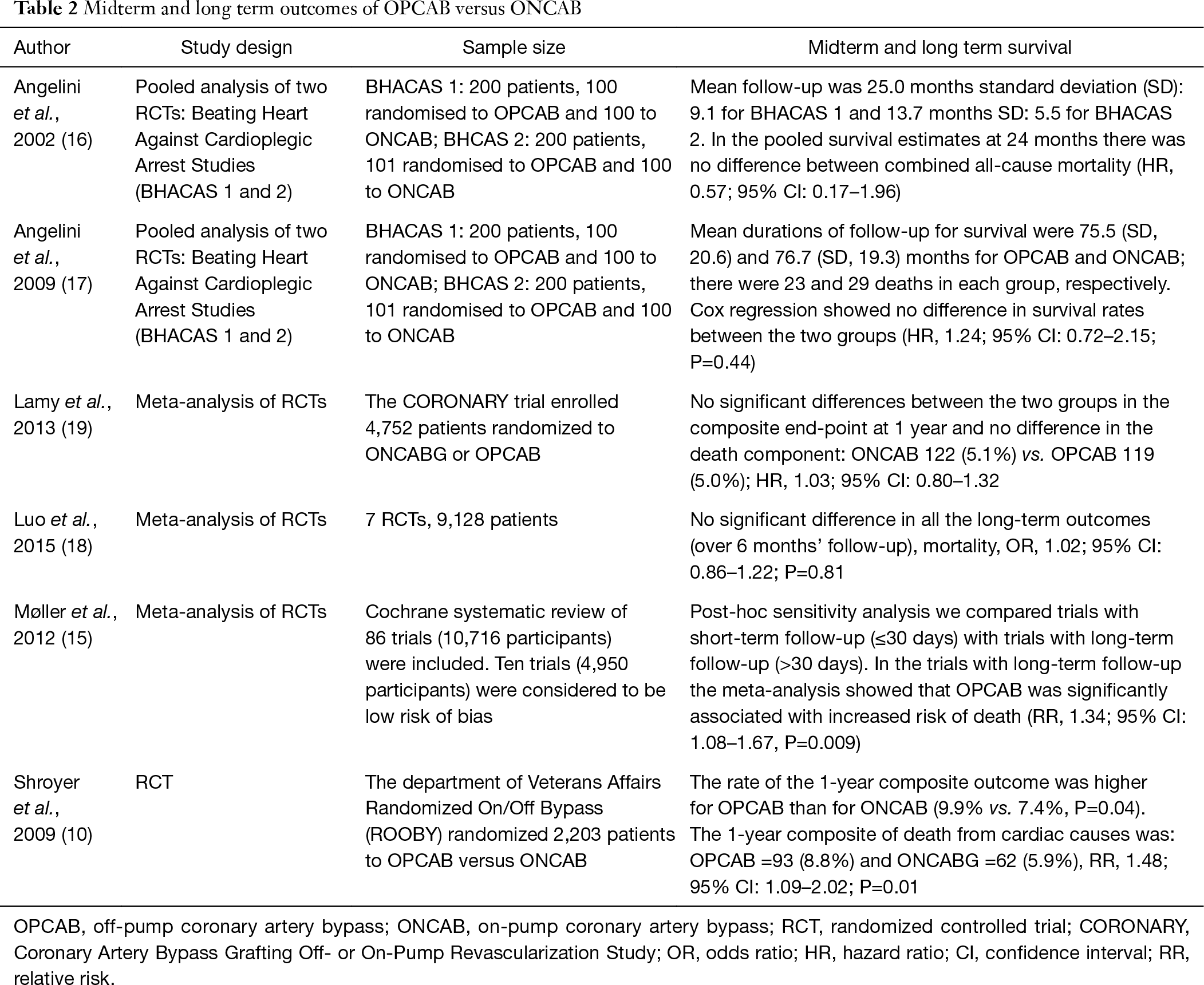


Current Outcomes Of Off Pump Versus On Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Evidence From Randomized Controlled Trials Fudulu Journal Of Thoracic Disease



Preoperative Membranous Urethral Length Measurement And Continence Recovery Following Radical Prostatectomy A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis European Urology



Who Saw This In The San Francisco Chronicle In The Past Week Ppt Download
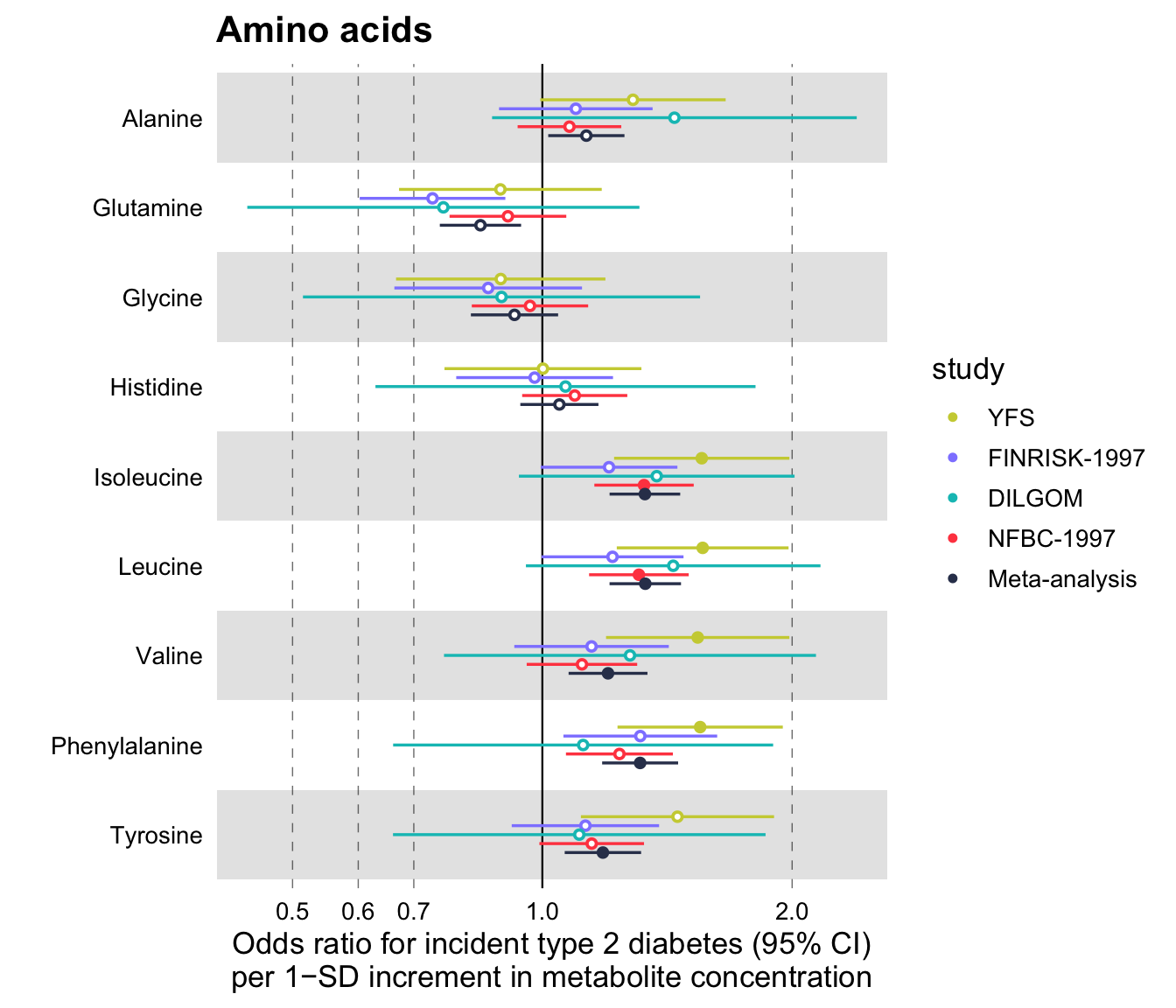


Using Ggforestplot Ggforestplot


Drmeta


Plos One Influence Of Clinicopathological Characteristics And Comprehensive Treatment Models On The Prognosis Of Small Cell Carcinoma Of The Cervix A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis
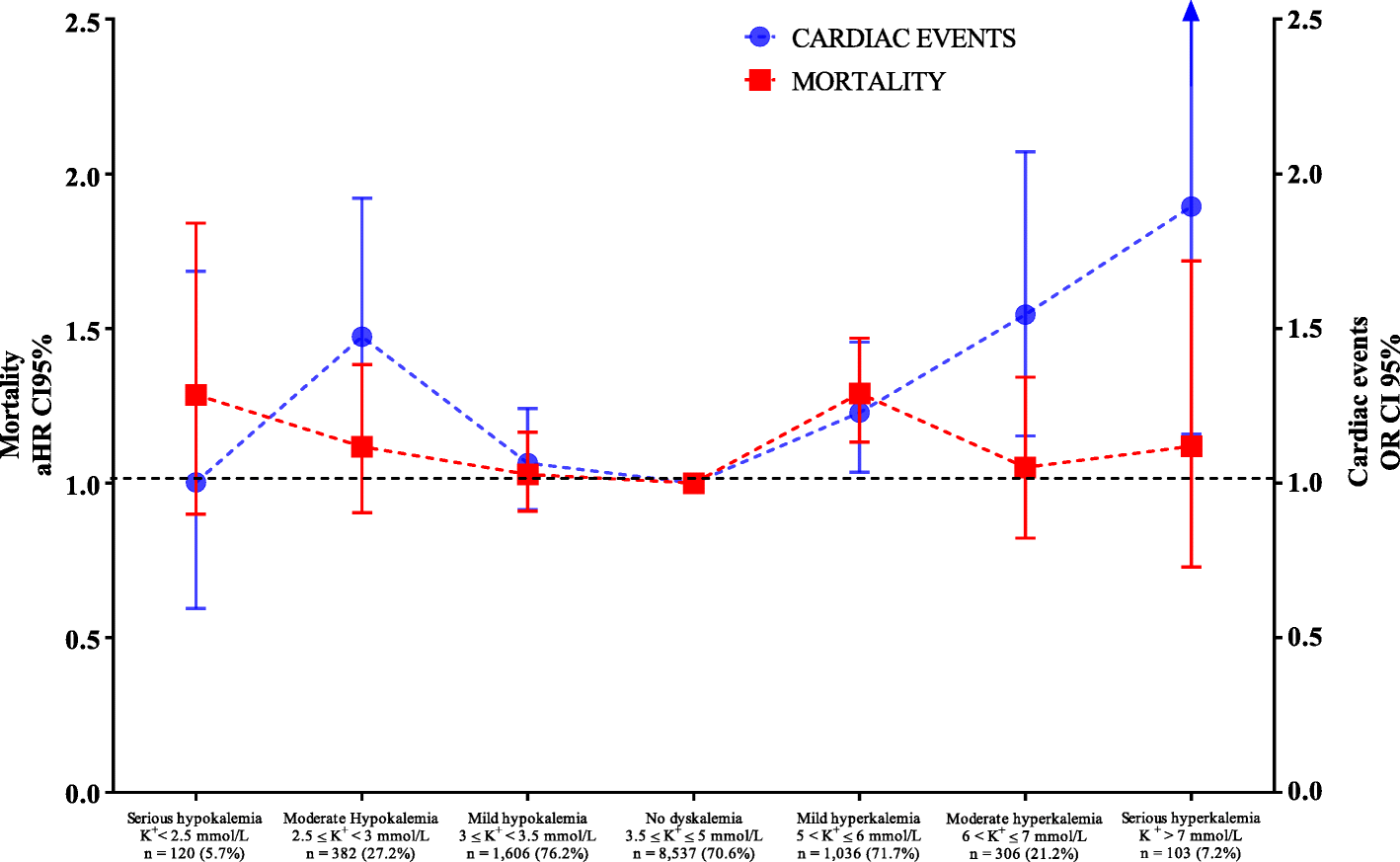


Influence Of Dyskalemia At Admission And Early Dyskalemia Correction On Survival And Cardiac Events Of Critically Ill Patients Critical Care Full Text


Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies



Survival Analysis In R



Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube



Assessing Heterogeneity Of Treatment Effect Estimating Patient Specific Efficacy And Studying Variation In Odds Ratios Risk Ratios And Risk Differences Statistical Thinking



Ctspedia Ctspedia Clinaegraph001



Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow



Retrospective Cohort Study Wikipedia



Hazard Ratio Vs Relative Risk Page 2 Line 17qq Com
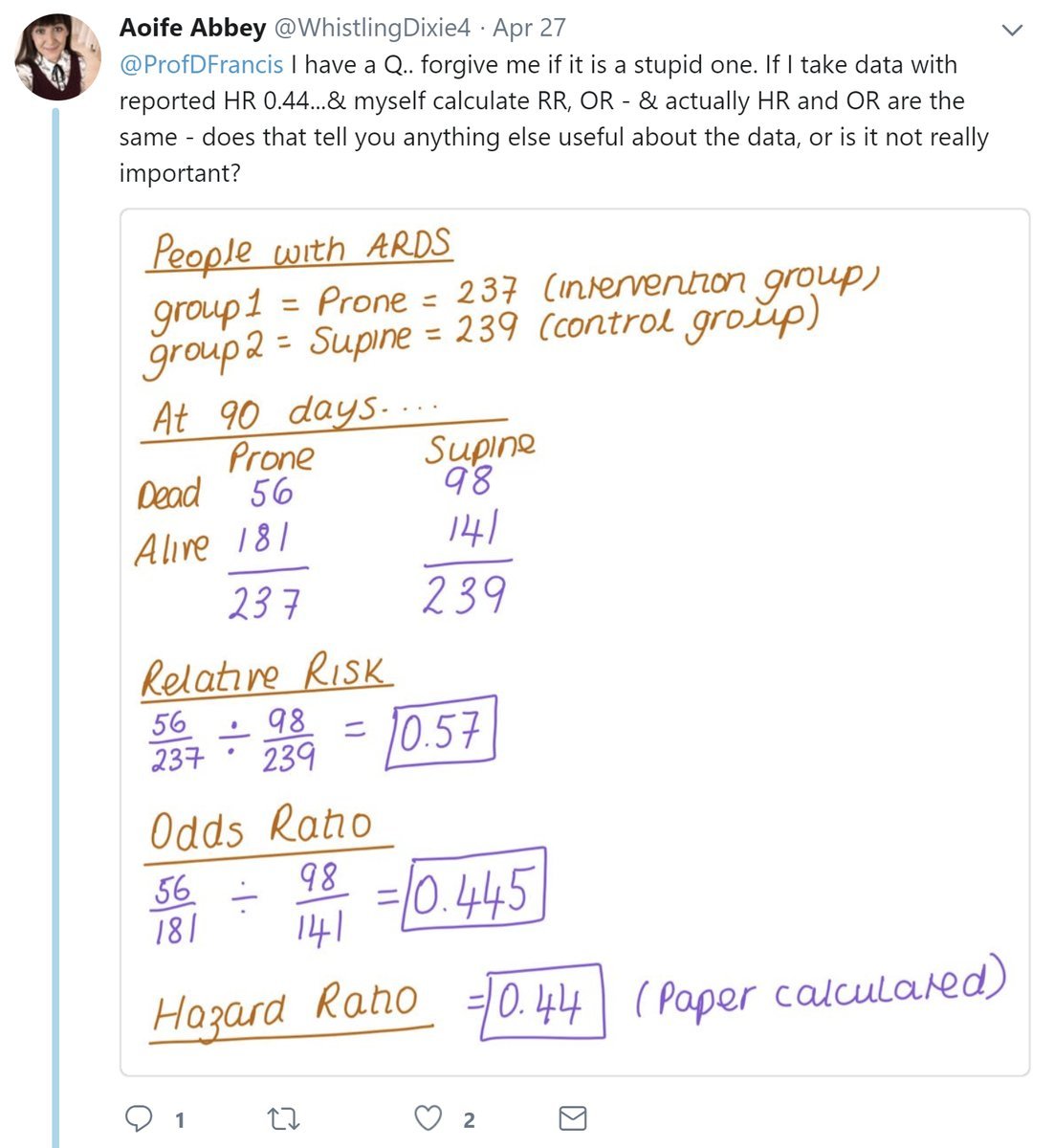


Prof Darrel Francis Mk Cardiofellows Great Again The Hazard Ratio Is In A Way The Best Thing We Could Calculate Because It Looks Along Every Instant In Time And



Time Trends In Incidence Comorbidity And Mortality Of Ischemic Stroke In Denmark 1996 16 Neurology


Who Saw This In The San Francisco Chronicle In The Past Week Ppt Download



Auswertung Epidemiologischer Studien



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿