= sin π 2 (cos arcsin x) − cos π 2 (sin arcsin x) =\sin\dfrac \pi 2 (\cos\arcsin x) \cos\dfrac \pi 2 (\sin\arcsin x) = sin 2 π (cos arcsin x) − cos 2 π (sin arcsin x) =Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators
3
π/2 angle
π/2 angle-The trigonometric reduction formulas help us to "reduce" a trigonometric ratio to a ratio of an acute angleIf the acute angle is a common angle, this technique helps us to find the ratio For example, imagine you need to find cot 300° We can say that 300° =270°30° ByDie reelle Exponentialfunktion exp R(x) = ex Satz i) F ur x




Vychislite Cos 3p 2 A Tg P 2 A Sin P 2 A Ctg 3p 2 A Ctg P 2 A Shkolnye Znaniya Com
Π/2 238 likes Personal Blog Sections of this page Accessibility HelpFur spitze Winkel 0¨ < α < π/2 ¨uber Verh ¨altnisse in rechtwinkligen Dreiecken definiert sind, die Ausdehnung auf stumpfe Winkel π/2 < α < π erfolgte dann durch sinα = sin(π − α) und cosα = −cos(π − α) F¨ur spitze Winkel 0 < α,β < π/2 deren Summe ebenfalls spitz ist, also αβ < π/2 kann man beide Additionsformeln aus derTrigonometry helps us find angles and distances, and is used a lot in science, engineering, video games, and more!
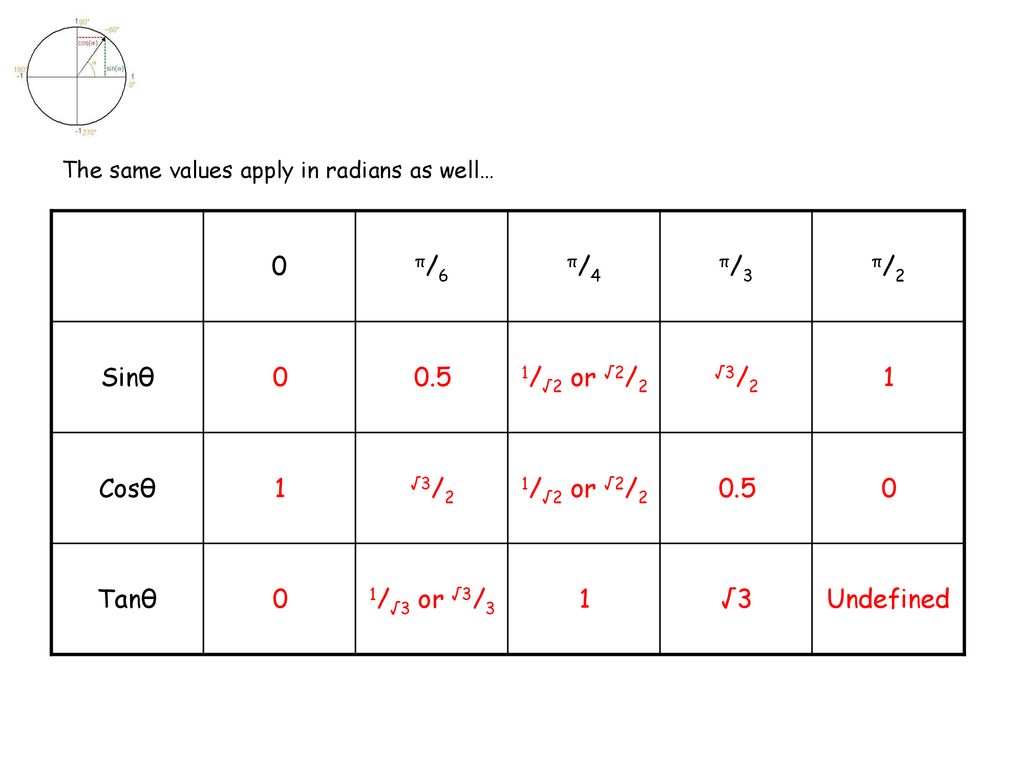
Prof Dr Karin Melzer Mathematik 1 Tabelle mit Werten von Sinus und Cosinus 0 bzw 360 15 30 45 60 75 90 105 360 360 bzw 0 345 330 315 300 285 270 255 x 0 = 2ˇ ˇ 12 ˇ 6 ˇ 4 ˇ 3 5ˇ 12 ˇ 2 7ˇ 12 x 2ˇ 2ˇ= 0 23ˇ 12 11ˇDefinition und Herleitung Wir wissen bereits, dass die Tangens und Kotangensfunktion die Definitionsmenge = {} bzw = {} und die Ziel und Wertemenge = haben Die beiden Funktionen sind surjektiv, jedoch nicht injektiv, da unterschiedliche Argumente existieren, die auf die gleichen Funktionswerte abbildenInsbesondere sind sie auch nicht bijektiv und damit nicht umkehrbarπ/2 の回転だとすべての関数が別の関数との関係を得られる。 π または 2π の回転だと、同じ関数内での関係となる。 π/2 の移動
Math 1 Übung 6 prof dr thoralf johansson, hs koblenz, übungen mathematik übungen mathematik serie berechnen sie die reellen nullstellen für die funktionenWir wissen bereits, dass die Sinus und Kosinusfunktion die Definitionsmenge = und die Zielmenge = haben Insbesondere sind beide Funktionen nicht bijektiv, da sie weder injektiv noch surjektiv sindZur Erinnerung Eine Funktion ist surjektiv, wenn sie jedes Element der Zielmenge trifft und eine Funktion ist injektiv, wenn unterschiedliche Argumente auf unterschiedliche FunktionswerteI guess this question rose in your mind while solving numerical problems in Physics p I'm gonna explain it to you, assuming that from mathg/math you mean the acceleration due to gravity near the surface of the earth We know that the value o




Sin P 2 A Sin P A Cos P A Sin 2p A Sprostiti Viraz Shkolnye Znaniya Com
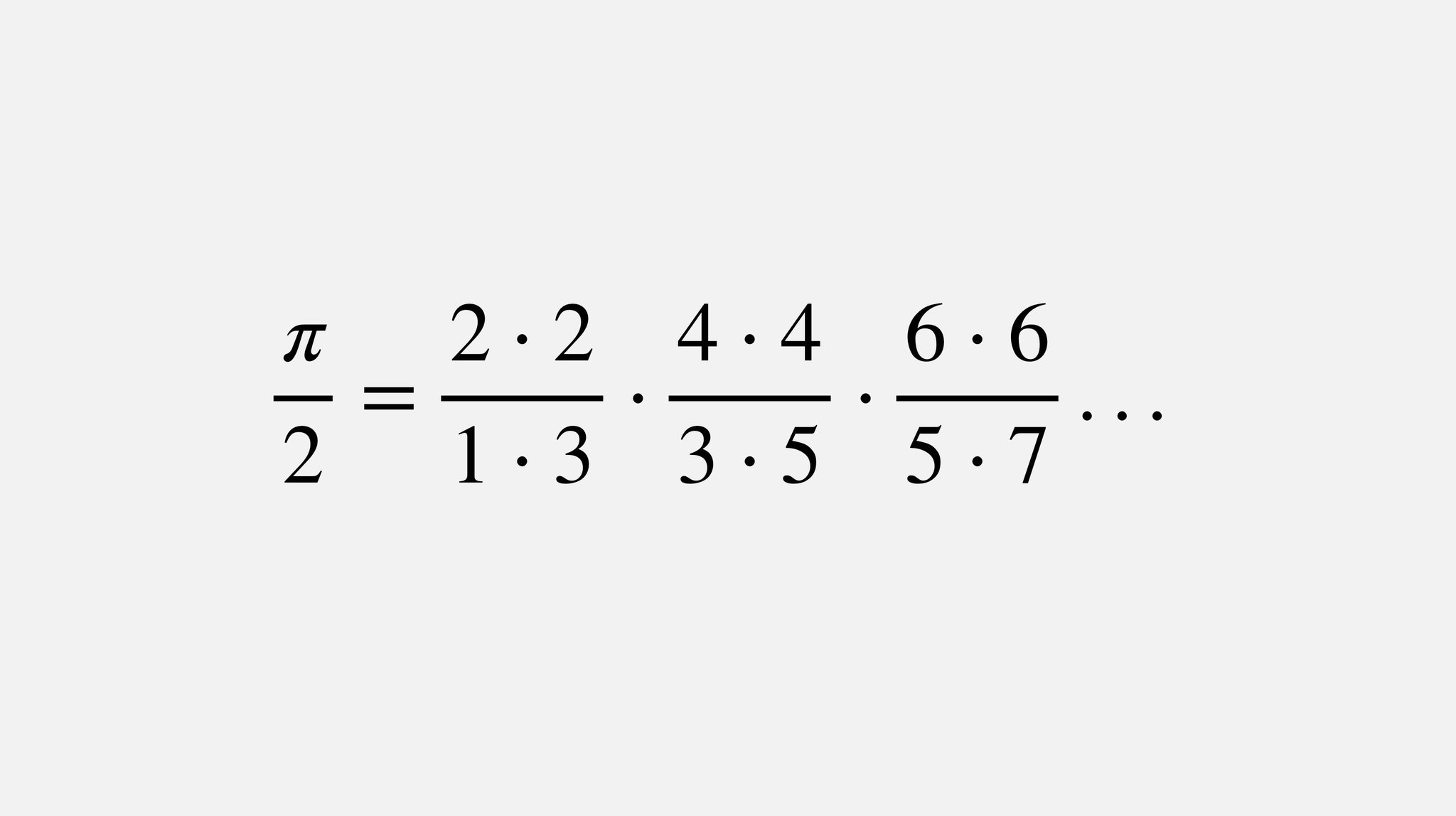



Fermat S Library John Wallis Devised This Beautiful Formula For P In 1655 It Is The Infinite Product Of Even Numbers Squared Divided By Their Two Adjacent Odd Numbers T Co Citnoitrll
Trigonometry AnglesPi/2 By the definition of the functions of trigonometry, the sine of is equal to the coordinate of the point with polar coordinates , giving Similarly, , since it is the coordinate of this point Filling out the other trigonometric functions then gives Weisstein, Eric W "Trigonometry AnglesPi/2" Inverse Trigonometric Formulas Trigonometry is a part of geometry, where we learn about the relationships between angles and sides of a rightangled triangleIn Class 11 and 12 Maths syllabus, you will come across a list of trigonometry formulas, based on the functions and ratios such as, sin, cos and tanSimilarly, we have learned about inverse trigonometry concepts alsoRightAngled Triangle The triangle of most interest is the rightangled triangleThe right angle is shown by the little box in the corner




Ex 7 10 5 Evaluate 0 Pi 2 Integral Sin X 1 Cos2 X Dx
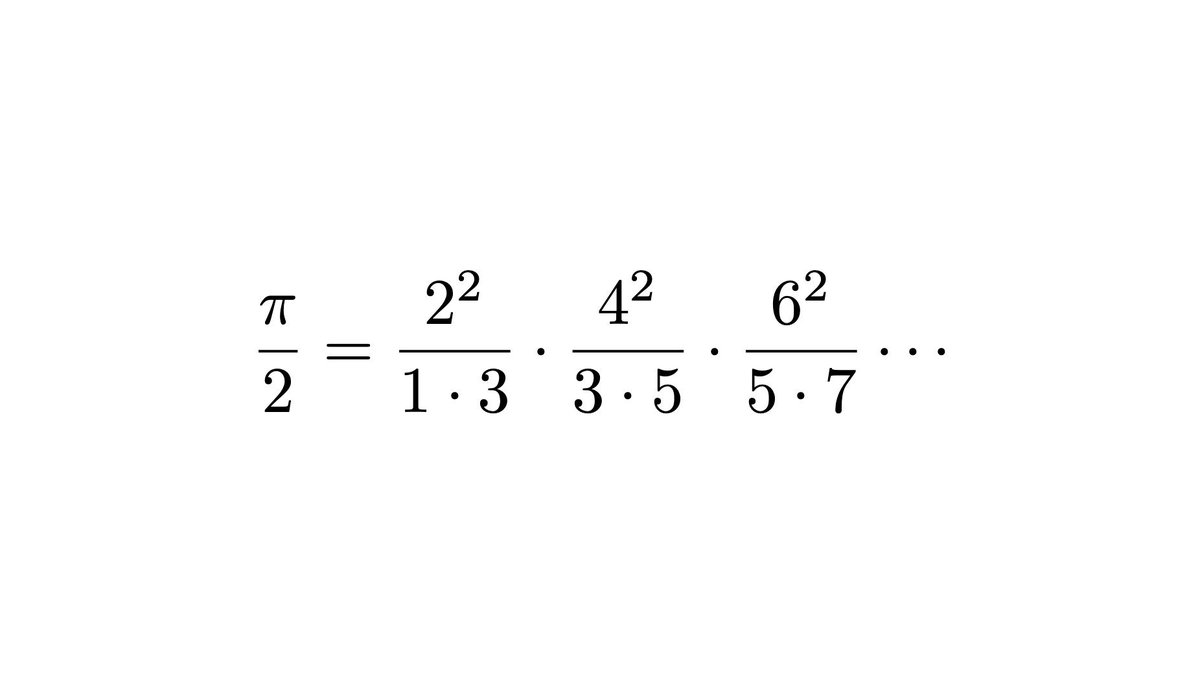



Berger Dillon Pa Twitter The Wallis Formula P 2 Is The Infinite Product Of Even S Squared Divided By Its Two Adjacent Odds
For (x, y) in quadrant 4, π/2 < θ < 0 クワドラント間の境界上にある点の場合は、次の戻り値になります。 For points on the boundaries of the quadrants, the return value is the following y が 0 で x が負数でない場合は、θ = 0。π / 2 rad τ / 4 rad Circumference C of a circle of radius r C = 2πr C = τr Area of a circle A = πr 2 A = τr 2 / 2 Recall that the area of a sector of angle θ (measured in radians) is A = θr 2 / 2 Area of a regular ngon with unit circumradius A = n / 2 sin 2π / n A = n / 2 sin τ / n Volume of an nballIn der Mathematik, insbesondere in den Gebieten Analysis, Differentialgeometrie und Differentialtopologie, ist ein Diffeomorphismus eine bijektive, stetig differenzierbare Abbildung, deren Umkehrabbildung auch stetig differenzierbar ist Dabei können die Definitions und Zielbereiche der Abbildung offene Mengen des endlichdimensionalen reellen Vektorraums R n
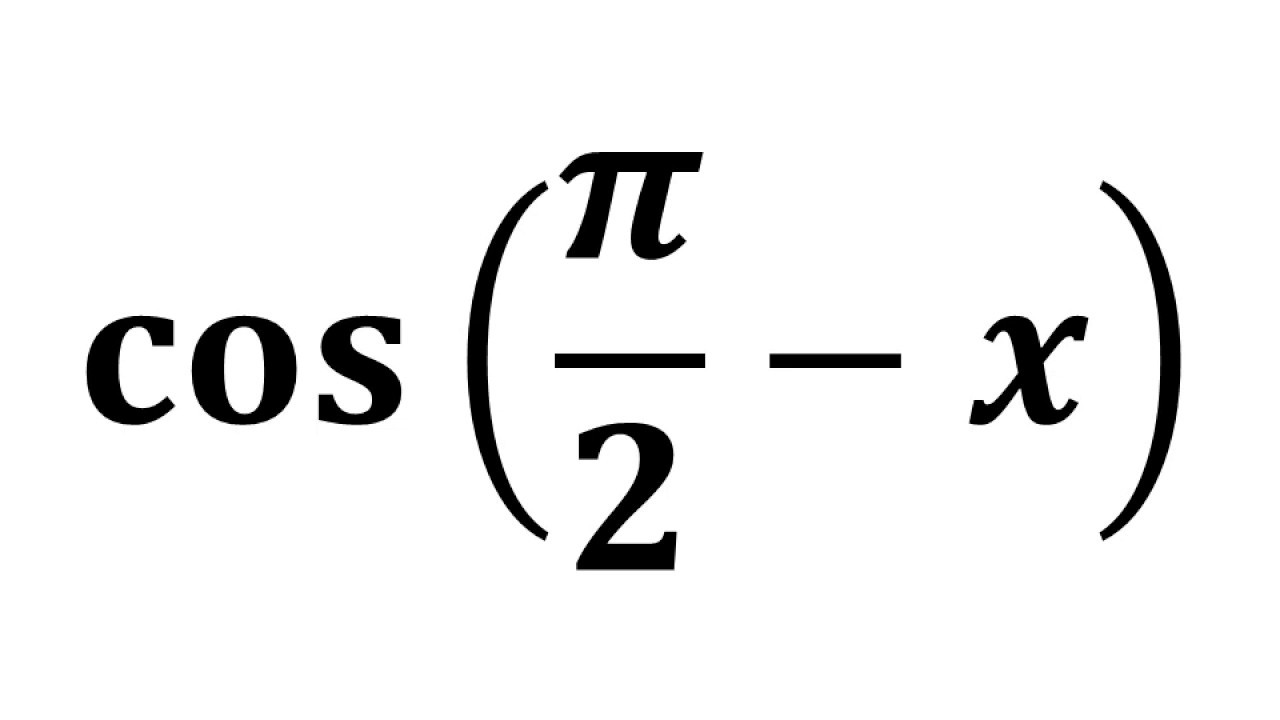



Sec Pi 2 X Sec Pi 2 Theta Youtube



Vertices 60 Biscribed Truncated Icosahedron Extreme Distribution Images A Critical Points Scheme For Generating Uniformly Distributed Points On A Sphere Geogebra
π/2 π/2φ 0 ΠΡΟΣΟΧΗ ͘ ΑΛΛΑΖΕΙ Ο ΤΡΙΓΩΝΟΜΕΤΡΙΚΟΣ ΑΡΙΘΜΟΣ ημͿπ/2φ= σʑνφ ή σʑνφ=ημͿπ/2φ σʑνͿπ/2φ= ημφ ή ημφ=σʑνͿπ/2φ εφͿπ/2φ= σφφ ή σφφ=εφͿπ/2φ σφͿπ/2φ= εφφ ή εφφ=σφͿπ/2φProof 1 The simplest way to prove cos(π/2 x) = sin x is to put A = π/2 , B = x in the trigonometric formula cos(AB) = cos A cos B sin A sin BEuler found the exact sum to be π 2 / 6 and announced this discovery in 1735 His arguments were based on manipulations that were not justified at the time, although he was later proven correct He produced a truly rigorous proof in 1741




Problem With Directed Angles Which Sum To Pi Over 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Integration 0 P 2 X Sinx Cosx Brainly In
Learn how to solve problems about cofunction identities in trigonometry This article also includes formulas, proofs, and examples with solutions that can help you fully apply the cofunction trigonometric identitiesTan ( π 2) tan ( π 2) Schreibe tan( π 2) tan ( π 2) mithilfe von Sinus und Kosinus um sin(π 2) cos(π 2) sin ( π 2) cos ( π 2) Der genau Wert von cos( π 2) cos ( π 2) ist 0 0 sin(π 2) 0 sin ( π 2) 0 Der Ausdruck enthält eine Division durch 0 0 Der Ausdruck ist nicht definiert Undefiniert 10 * π = 2^2 * π * h h = 25 mfg GoldundSilberliebichsehr Beantwortet von goldusilberliebich 2,5 k Ich habe c) so gerechnet Kommentiert von probe Warum steht da eine 2 vor dem pi vor dem Integral Die gehört da nicht hin Sonst richtig




Evaluate Integral From P 2 To P 2 X 2 Sin Xdx Cbse Class 12 Sa




Solve Equation Cos A Cos B Cos A B Frac18 Over 0 A B Frac Pi2 Mathematics Stack Exchange
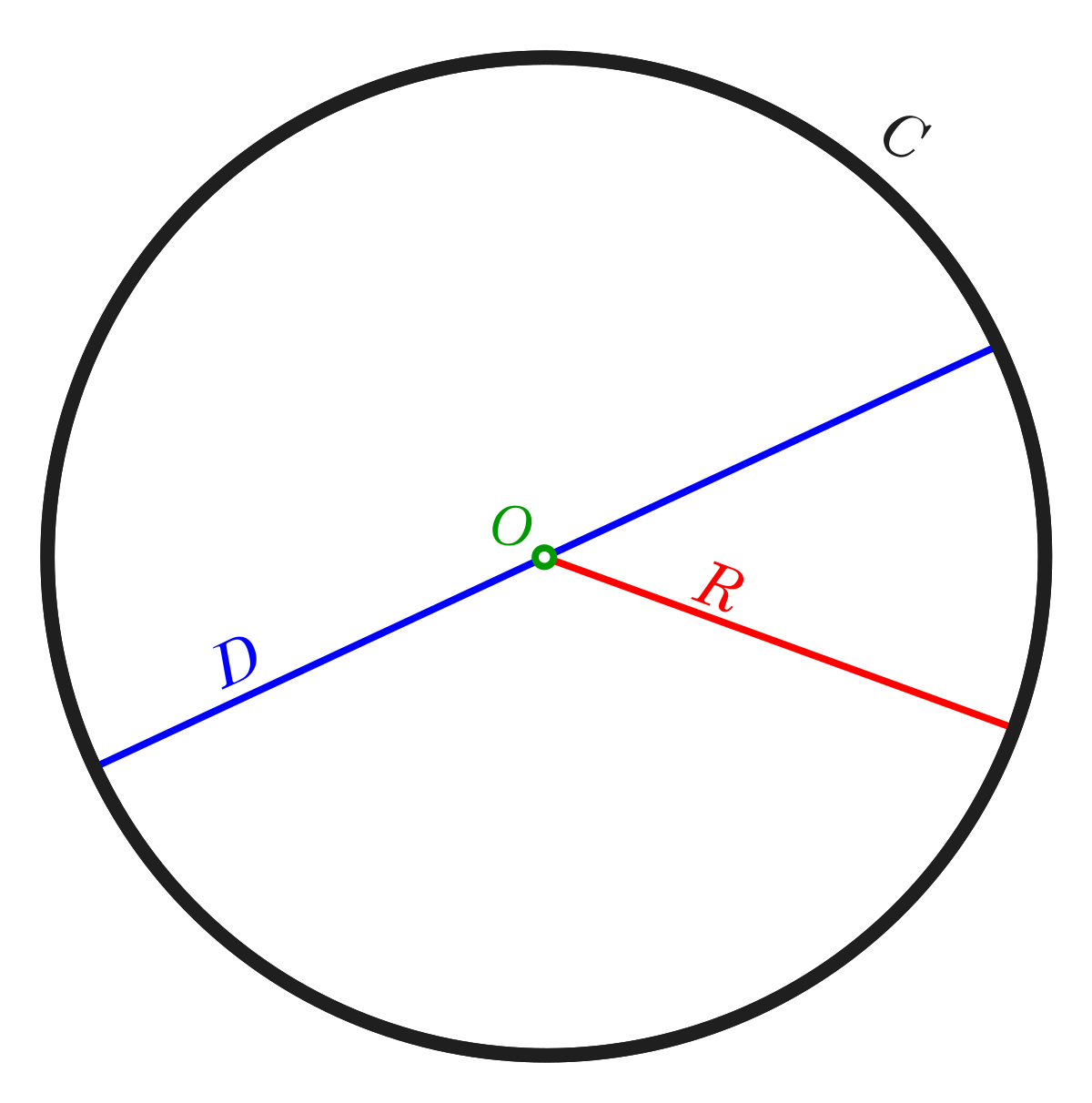
Die natürliche Einheit zum Messen von Winkeln ist das Bogenmaß, die man aus der Formel für den Kreisumfang erhält c = 2 π r, wobei r der Radius ist Wenn r = 1, dann ist c = 2 πSomit ist das Bogenmaß definiert, dass der Kreis 2 π als Bogenmaß ist und das sind auch 360° 1 Bogenmaß (radiant) = 360 / 2 π = 57, GradX→ π 2 ln(π 2 −x) tanx 0 = lim0 x→ 2 µ −1 π 2 −x ·cos2 x ¶ 0 = lim0 x→π 2 2cosxsinx −1 = 0 (d) Hier ist lim x→0 xtanx = lim x→0 etanxlnx = exlim →0 (tanxlnx) Die letzte Umformung ist wegen der Stetigkeit der Exponentialfunktion m¨oglich Also berechnen wir den Grenzwert lim x→0 (tanxlnx) Es ist lim x→0 (tanxlnx) = lim x→0 lnx ctanx = lim x→0 −sin2 x x 0 = lim0Monte Carlo simulation on MS Excel Find ratios of areas, find Pi (π)Here is the link to the excel file https//drivegooglecom/file/d/1NVExO4E2hPZYxn6t0lx




General Solution Of Tantheta Tan Pi 2 Theta 2 Is
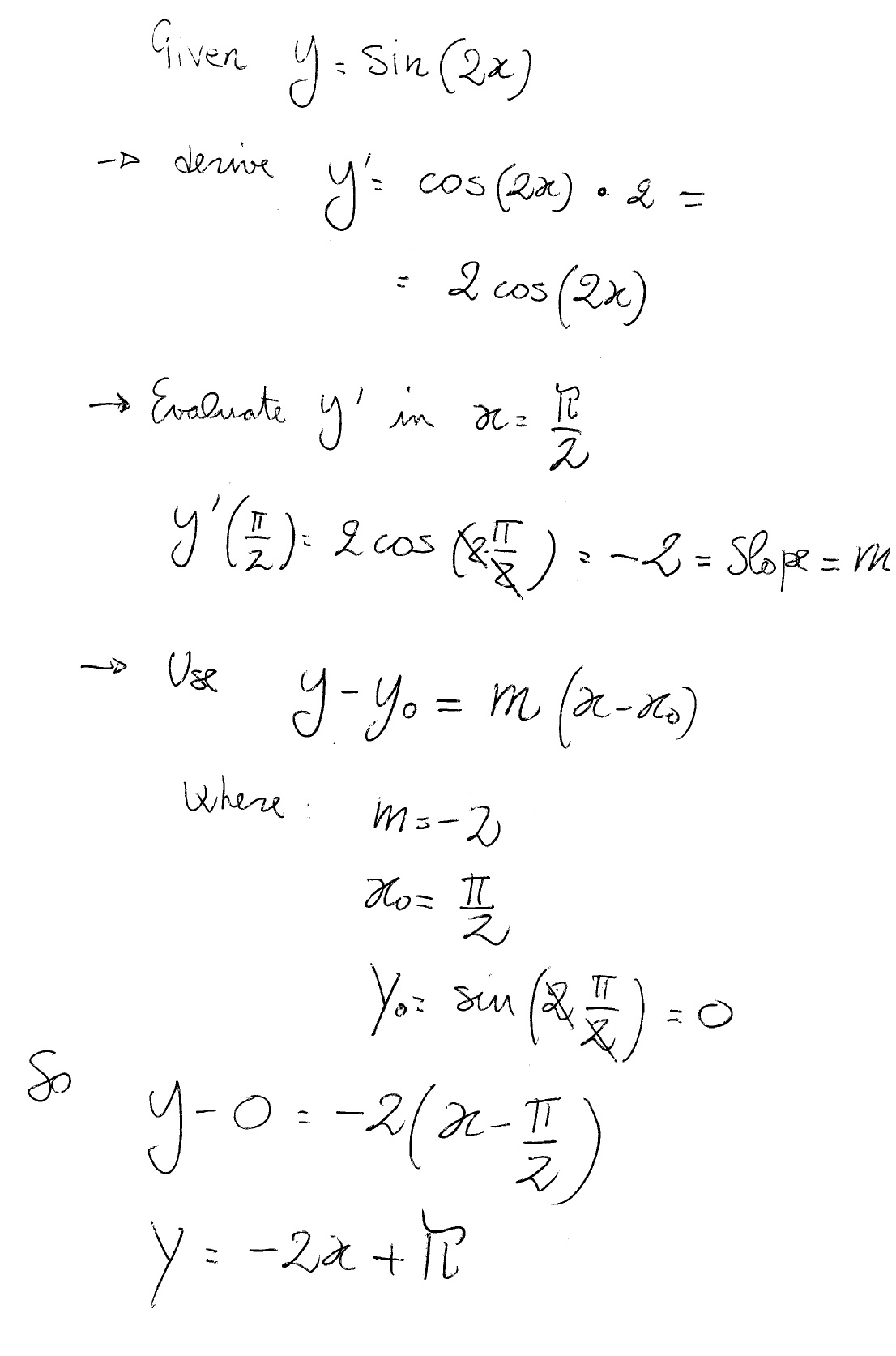



How Do You Find The Equation Of The Tangent Line To Y Sin 2x At X Pi 2 Socratic
Auf (0,π/2) ist g differenzierbar mit g0(x) = 1 p 1−cos2(x) ·(−sinx)− −1 p 1−sin2(x) ·cosx = 1 p sin 2(x) ·(−sinx)− −1 p cos ( x) ·cosx = −sinx sin( cosx cos(= −11 = 0, da sinx > 0,cosx > 0 fur alle¨ x ∈ (0,π/2) Folglich ist g auf (0,π/2) konstant mit g(x) = g(π/4) = arcsin(1 2 √ 2)−arccos(1 2 √Verwende, dass arcsin (1) = π 2 \sf \arcsin(1)=\dfrac{\pi}{2} arcsin (1) = 2 π Betrachte hierzu den obigen Graphen von Arkussinus x = − π 2 \displaystyle \sf x=\dfrac{\pi}{2} x = − 2 πA = π r 2 {\displaystyle A=\pi r^ {2}} where A is the area of a circle and r is the radius V = 4 3 π r 3 {\displaystyle V= {4 \over 3}\pi r^ {3}} where V is the volume of a sphere and r is the radius S A = 4 π r 2 {\displaystyle SA=4\pi r^ {2}} where SA is the surface area of a sphere and r is the radius




Aufgabe 1 Der Graph Der Funktion Ppt Herunterladen




Calculate The Value Of Tan Pi 2 Pi 6 Brainly In
Annäherung an π 2 Mit den Schiebereglern kannst du den Radius des Kreises und die Anzahl Ecken des Vielecks verändern 1 Die Fläche des Vielecks ist kleiner als die Kreisfläche Erhöhe die Anzahl Ecken Beobachte, wie sich die braune Vieleckfläche immer mehr der Kreisfläche annähert 2 Formel Torus Volumen Radius V = 2 π 2 r 2 R V = 2 π 2 r 2 R r = 1 π V 2 R R = V 2 π 2 r 2 Formel umstellen Illustration bekommen Torus von oben / durchgeschnittenLim (x → π /2) tan2x/(xπ /2) At x = π /2 the value of the given function takes the form 0/0 Now put xπ /2=y so that x → π /2,y →0




Evaluate Lim X 0 Sin 2 P 2 Ax Sec 2 P 2 Bx Youtube



Tangensfunktion Lernen Mit Serlo
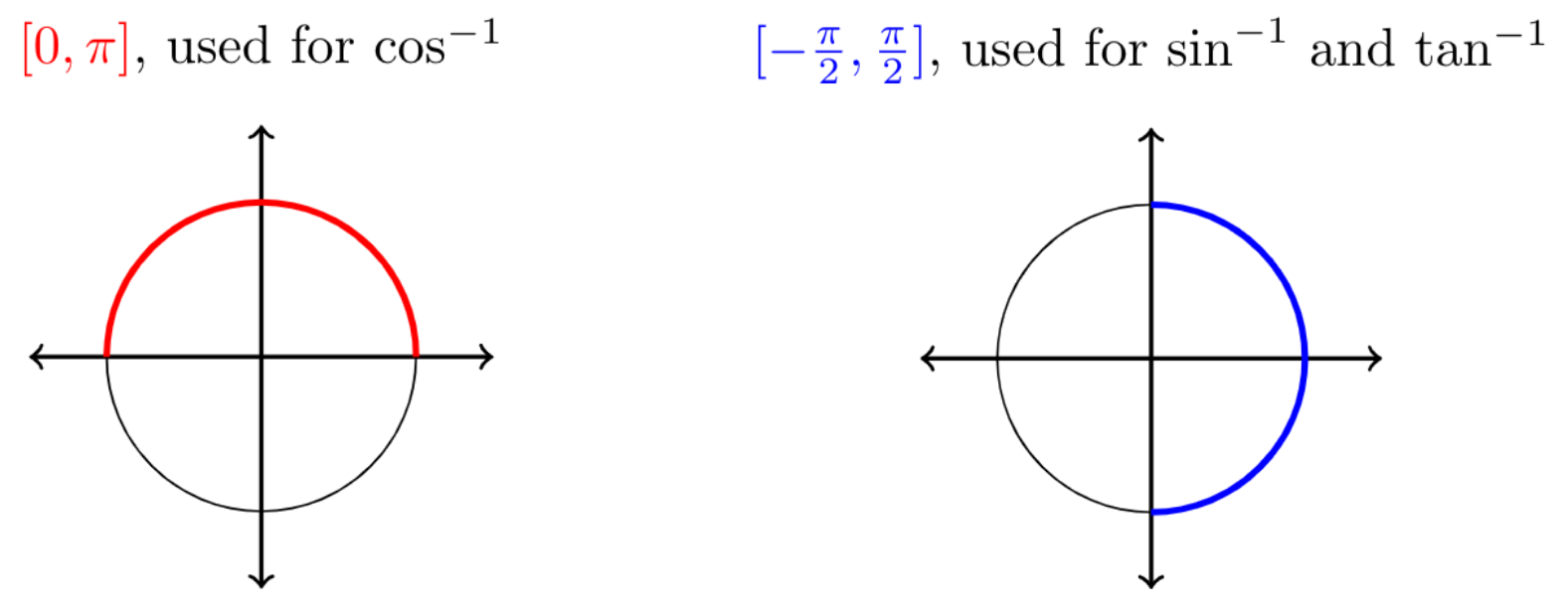
π 2 x ∈ R Ableitung und Integral (46) d dx arccotx = − 1 1x2, Z arccotxdx = xarccotx 1 2 log(1x2) Reihendarstellungen und Grenzwerte (47) arccotx = π 2 X∞ k=0 (−1)k1x2k1 (2k 1) x < 1 23 Arcussinus und Arcuscosinus arcsin −1,1 → −π/2,π/2, arccos −1,1 → 0,π Der Arcussinus ist f¨ur x ≤ 1 Ein Tunnel soll die Form eines Rechtecks mit aufgesetztem Halbkreis erhalten Wie groß ist die wenn der Umfang des Tunnels m betragen soll?Erfüllt Ein mathematisch nützlicher Zusatzeffekt ist, dass Winkel, bei denen der Tangens eine Polstelle hat, nämlich die Winkel ± 90 ∘ = ± π / 2, {\displaystyle \pm 90^{\circ }=\pm \pi /2\,,} durch ganz normale reelle Koordinaten spezifiziert werden können, nämlich durch ± π / 2 = arctan2 {\displaystyle \pm \pi /2=\operatorname {arctan2} } anstatt arctan {\displaystyle \operatorname
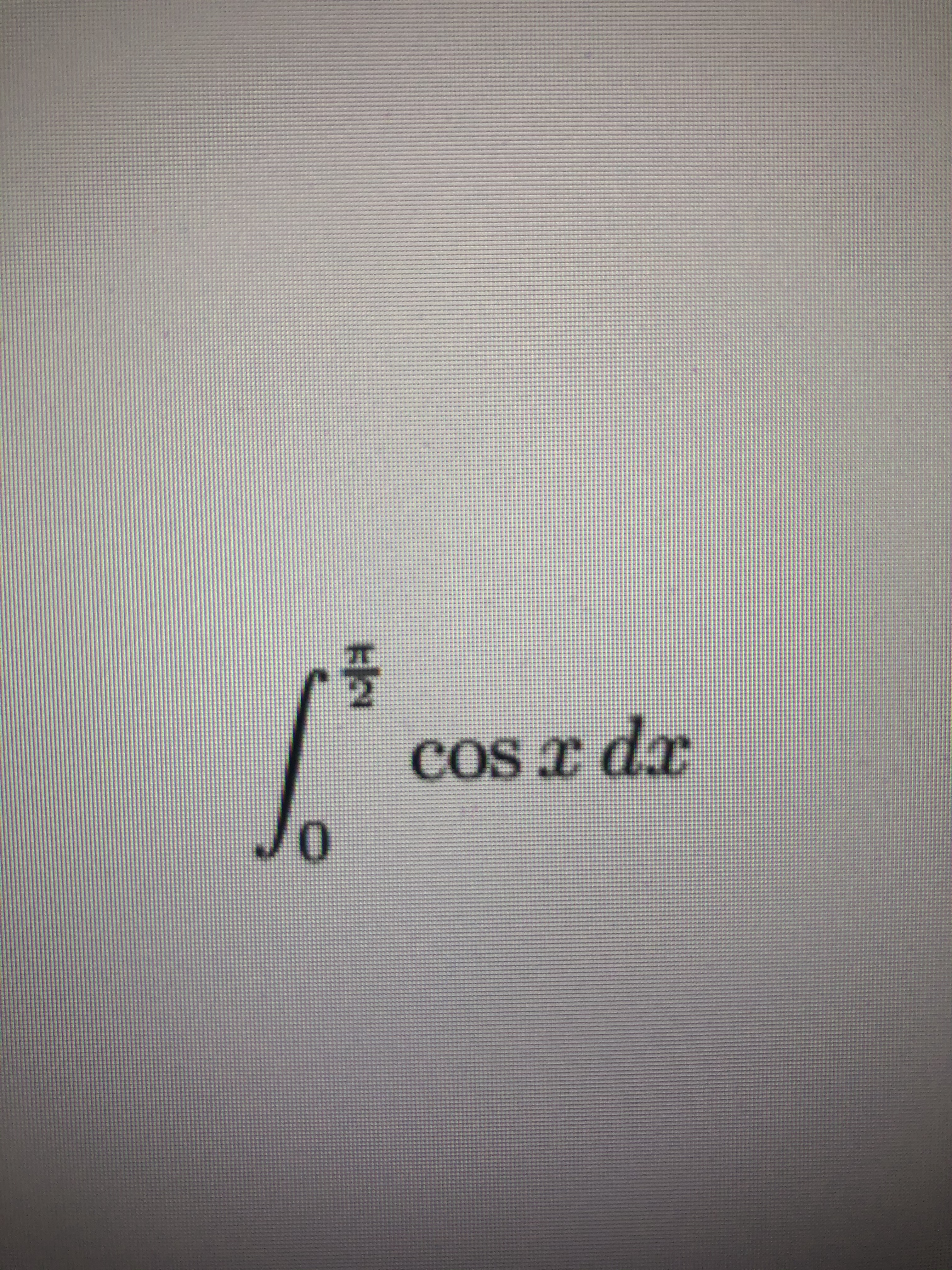



Answered P 2 Cosx Dx 0 Bartleby




Prove That Int Pi Sin 7x Sin 7x Cos 7x Dx Pi4
θ+π/2,θπの導き方 ここまで公式を解説してきましたが、正直言うと覚えなくても良いです。 その代わり、 公式の導き方を覚えておいてください。1 Rechnen mit komplexen Zahlen Komplexe Zahlen z 2 C abi (Normalform) a Realteil b Imagin¨arteil (b 2 R!) i imagin¨are Einheit, i2 = ¡1 gef¨ahrlicheThe number of solutions of the equation x 2 tanx = π/2 in the interval 0, 2π is ← Prev Question Next Question




97 44 Another Proof That Z 2 P2 6 Via Double Integration The Mathematical Gazette Cambridge Core




If Sin 8 3 5 On The Interval Frac P 2 Gauthmath
Die Tangensfunktion ist definiert als tan ( x) = sin ( x) cos ( x) \displaystyle \sf \tan (x)=\dfrac {\sin (x)} {\cos (x)} tan(x) = cos(x)sin(x) Der Tangens hat folgende Eigenschaften Die Nullstellen sind die gleichen wie beim Sinus, da dieser im Zähler des Bruches steht , − 3 π, − 2 π, − π, 0, π,



Solved Give A Proof For Cos Pi 2 X Sinx When 0 X Pi 2 Course Hero
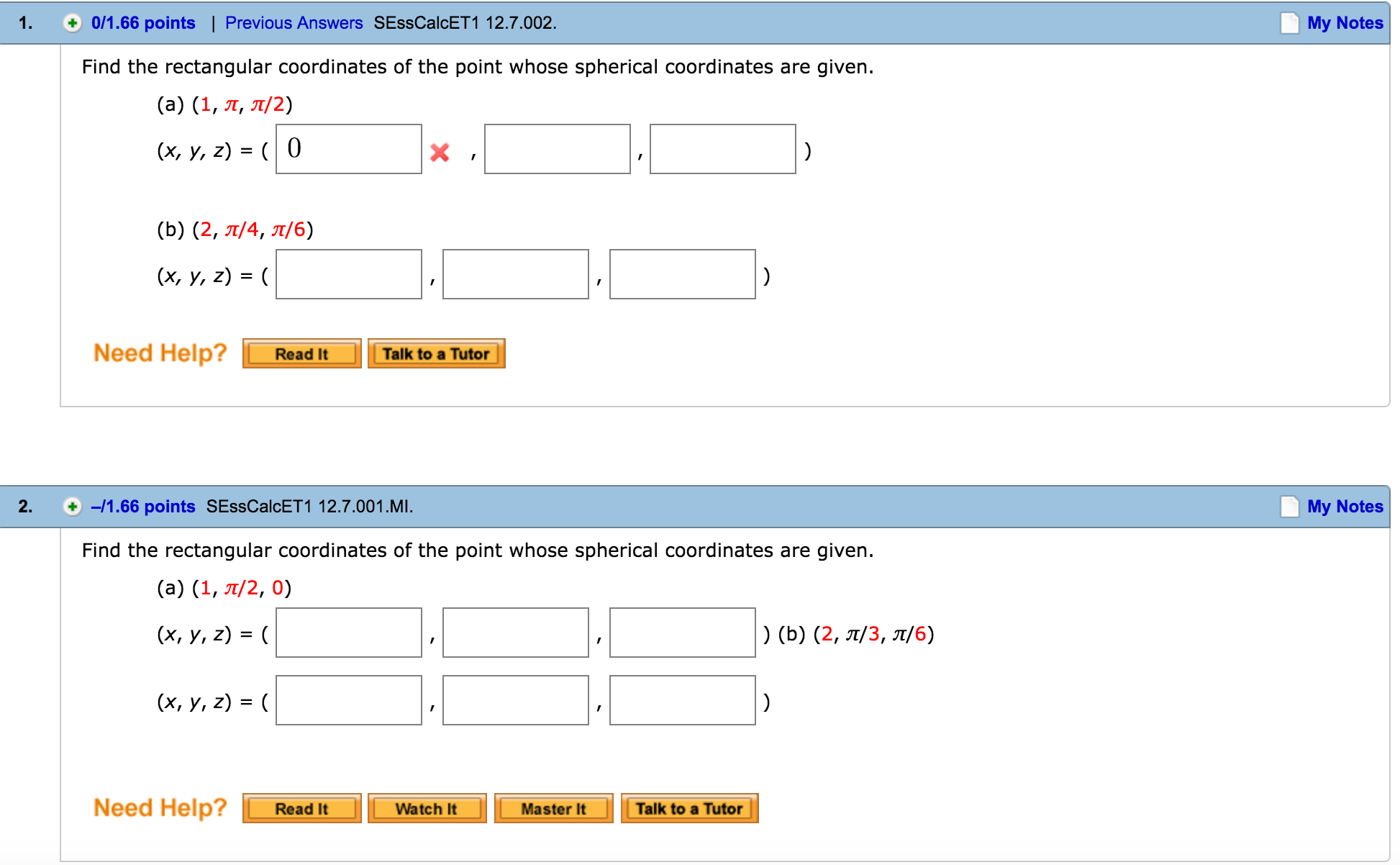



Find The Rectangular Coordinates Of The Point Whose Chegg Com




F X Cos X Sin X Find F P 2 And F P 4 Brainly In
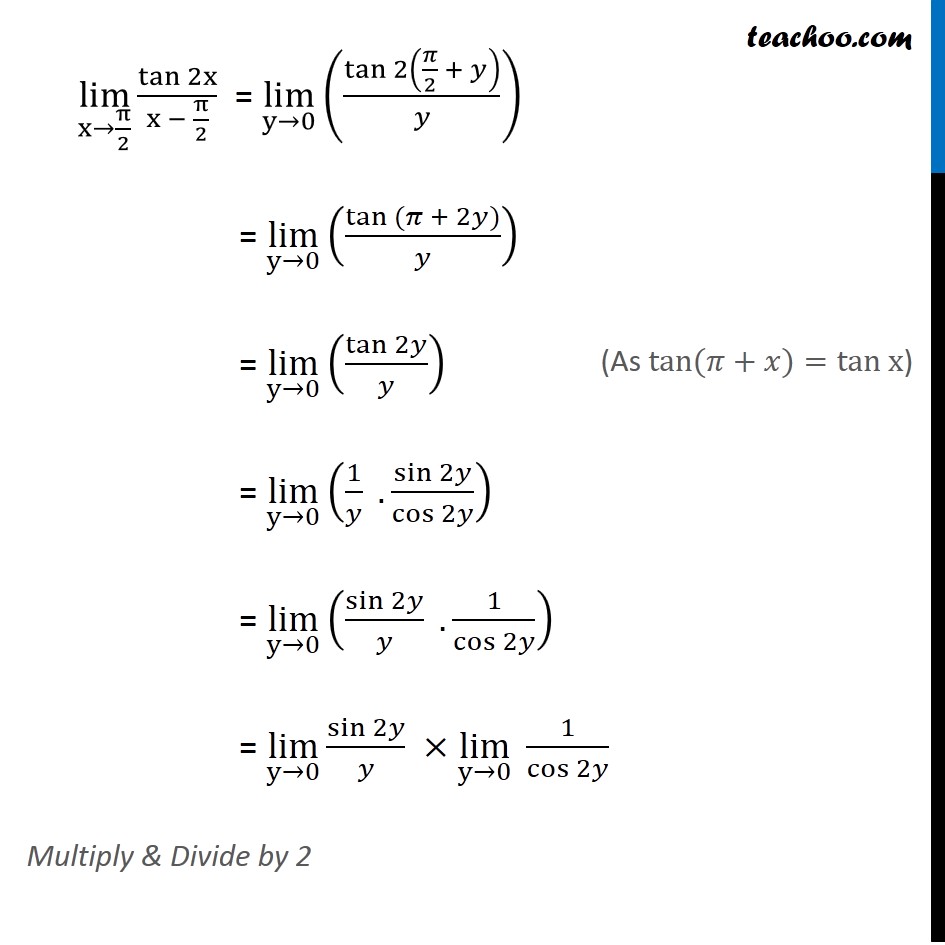



Ex 13 1 22 Lim X Pi 2 Tan 2x X Pi 2 Chapter 13 Class 11




Evaluate Int 0 Pi 2 X Dx Cos X Sin X



A Slice Of P As P Goes So Goes A Circle Finding P By Dr Vk Cantor S Paradise



Trigonometric Functions And Circles Trigonometric Functions High School Algebra Ii Unlocked 16




How Do You Find The Equation Of The Tangent Line To The Curve Y 2xsinx At Pi 2 Pi Socratic



Mfg Inverse Trigonometric Functions




Aufgabe 1 Der Graph Der Funktion Ppt Herunterladen
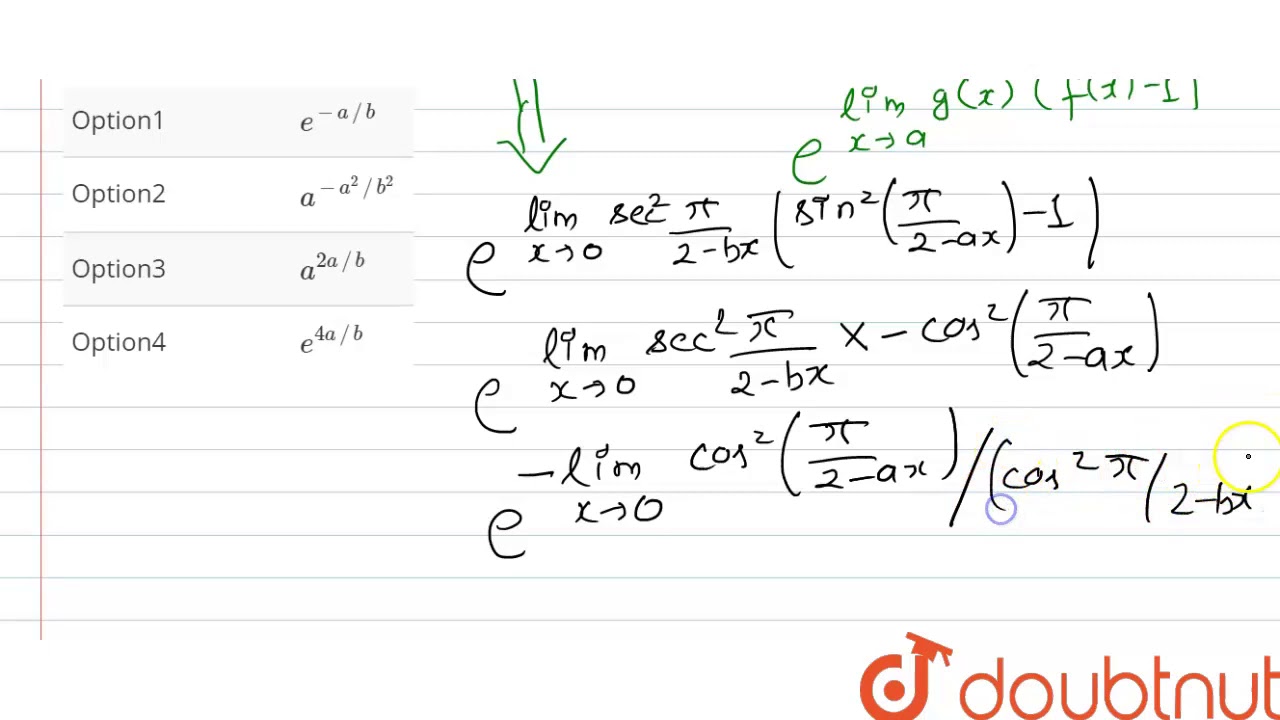



The Value Of Lim Xto0 Sin 2 Pi 2 Ax Sec 2 Pi 2 Bx Is Equal To Youtube




Ex 13 1 22 Lim X Pi 2 Tan 2x X Pi 2 Chapter 13 Class 11




If Sin X 5 3 And Pi2 X Pi Find The Value Of Sin X2



Immigration Settle Sensitive Sin Sin Pi 2 Bergenpianostudio Com




Geometric Proof Of Sin Frac Pi2 Theta Cos Theta For Theta Frac Pi2 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Using Roots Of Unity To Prove That Cos Frac Pi 2n Cos Frac 2 Pi 2n Cdots Cos Frac N 1 Pi 2n Frac Sqrt N 2 N 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Sin Pi 2 09 Cos Pi 2 09 Cos Pi 2 08 Cos Pi 2 2 Is Youtube



Solved What Is The Residue Of F Z Tan Z At Z 2 What Is The Residue Of F Z Z S I N Z 1 At Z 0 Course Hero




2 Consider The Double Integral T Xxsin Yd Gauthmath




P 2 Target D 2 10 40 Comparison Of F Aimm With Rwmh Amh Agm Download Table




3 Ways To Type The Pi Symbol Wikihow



2 Let F X 4 Sin X 1 2 Where P 2 X Chegg Com
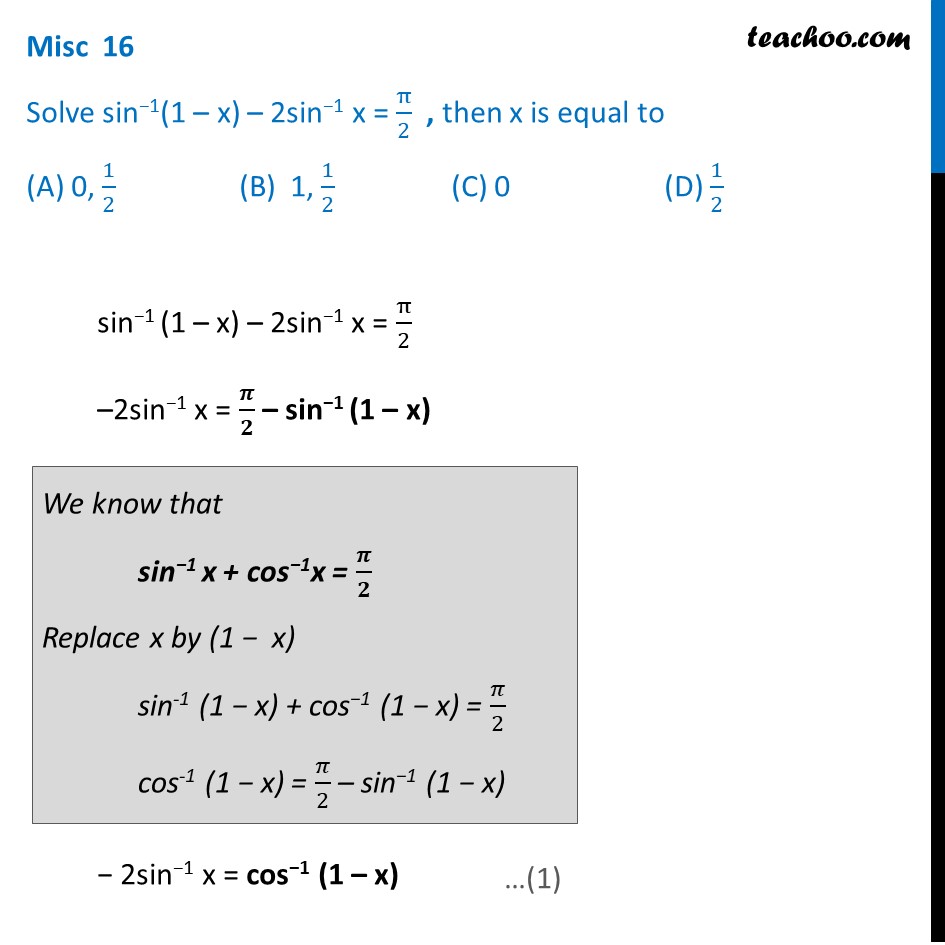



Solve Sin 1 1 X 2 Sin 1 X Pi 2 Then X Is Trigonometry




Fermi Surface In The Folded Bz P 2 Download Scientific Diagram



A Quasi Hybrid Dislocation With 8 1 P 2 And 8 2 0 001 Rd Download Scientific Diagram




Mathematical Function Graphics Programmer Sought




4 If Sin 8 5 13 And Frac P 2 8 P Gauthmath




Find The Value Of Lim X Pi 2 Cosx Pi 2 X Maths Limits And Derivatives Meritnation Com



Tinkutara Equation Editor Math Forum Question 805




Int 2 Pi 2 Pi 1 U 0 X Sin X 2 Delta X P Delta X P Mathrm D X Mathematics Stack Exchange




List Of Trigonometric Identities Wikipedia



3



Trigonometry Inverse Functions Ppt Download



2




Evaluate Int Pi 4 Pi 2 Cos2xlogsinxdx



G Pi 2 Physicsmemes




Mathematical Function Graphics Programmer Sought



Circumference Wikipedia




Sec Pi 2 Theta Find The Value Brainly In




The Value Of Cos Pi 2 2 Cos Pi 2 3 Cos Pi 2 10 Sin Pi 2 10 Is
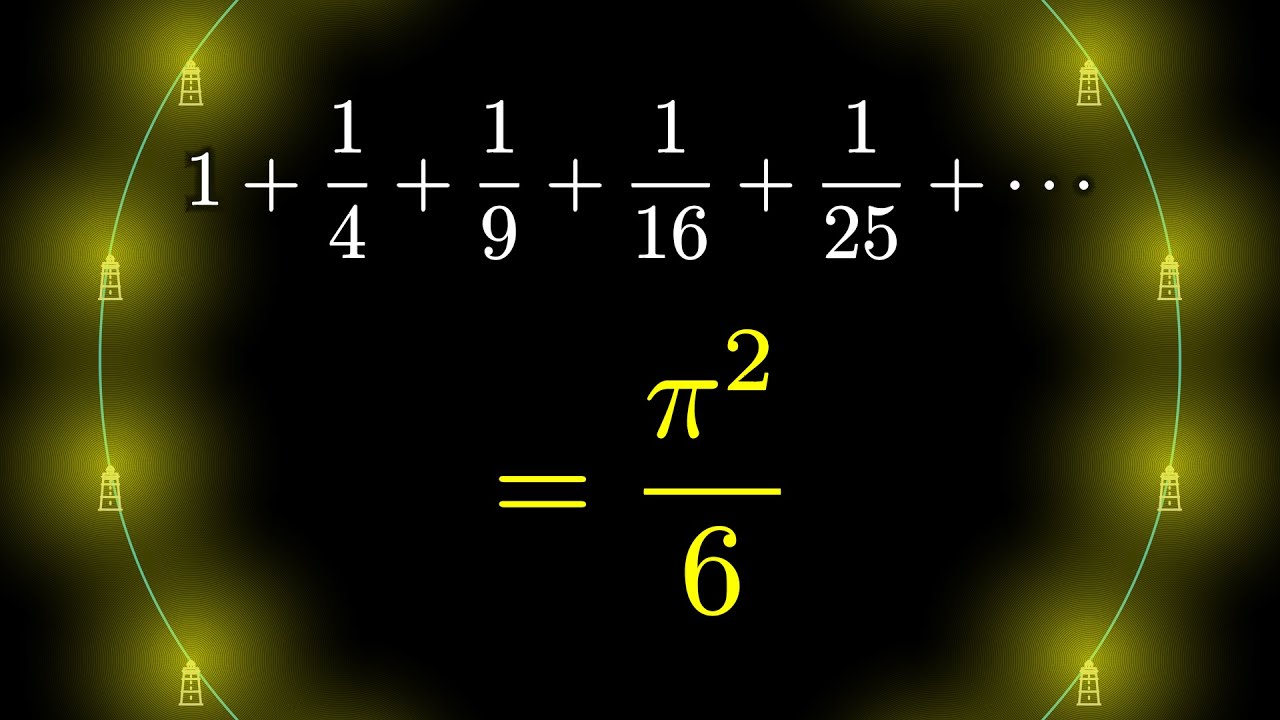



Why Is Pi Here And Why Is It Squared A Geometric Answer To The Basel Problem Youtube
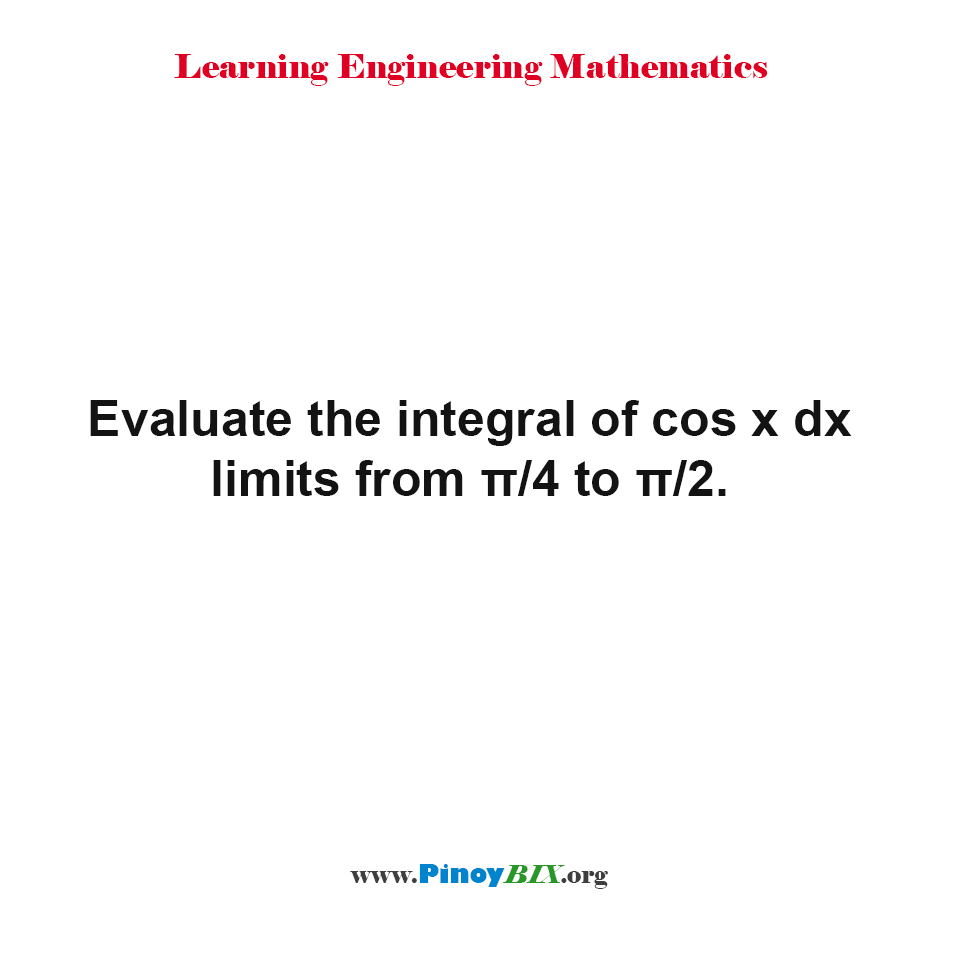



Solution Evaluate The Integral Of Cos X Dx Limits From P 4 To P 2
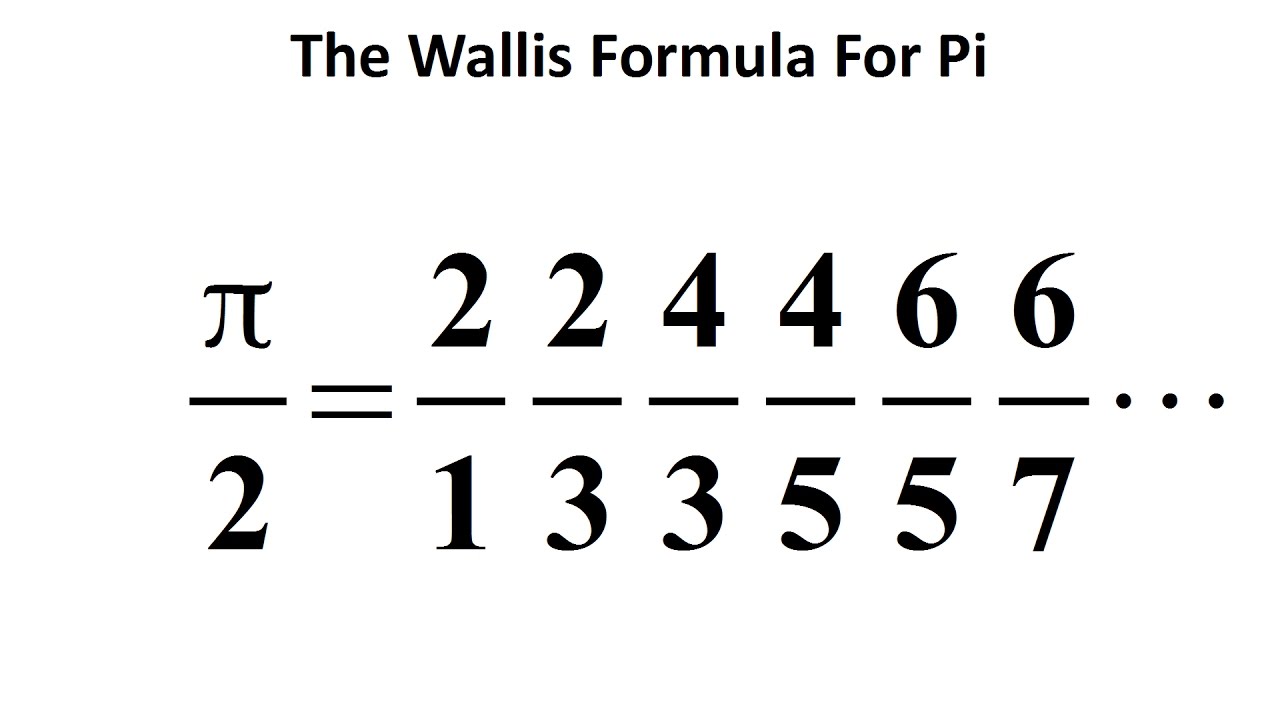



The Wallis Product Formula For Pi And Its Proof Mind Your Decisions




Evaluate Lim Xrarr Pi 2 Cosx Pi 2 X




Proving Left Frac 1 Sin X I Cos X 1 Sin X I Cos X Right N Cos N Left Frac Pi 2 X Right I Sin N Left Frac Pi 2 X Right Mathematics Stack Exchange



Ppt 1 Change Each From Radians To Degrees 13 P 6 B P 2 C P Powerpoint Presentation Id




Vychislite Cos 3p 2 A Tg P 2 A Sin P 2 A Ctg 3p 2 A Ctg P 2 A Shkolnye Znaniya Com



A Graph R 1 4cos8 R 1 4cos 8 For Chegg Com
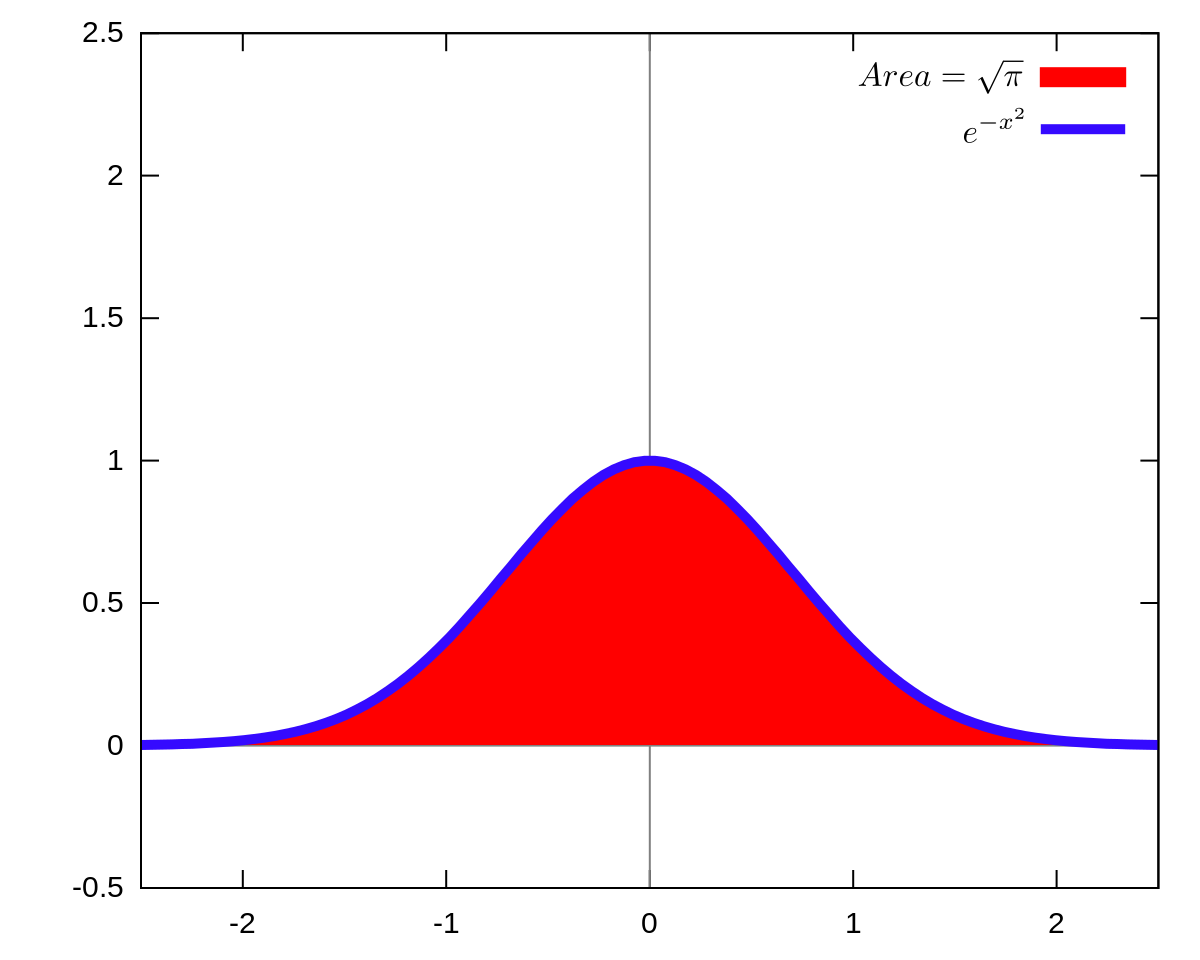



Gaussian Integral Wikipedia




Prove Cos X Sin 3 Pi 2 X Sin 3 Pi 2 X Cos Pi X 0 Maths Trigonometric Functions Meritnation Com




The X Y Shapes For Equilibrium Configuration With 1 Red 2 Green Download Scientific Diagram



Tinkutara Equation Editor Math Forum Question 805




European Pi 2 Font Fontpalace Com



Q Tbn And9gctg1mv4zqwzzx9es1vyuwisok4cikumrujuyo2nyqlvyw5qkqqv Usqp Cau




The Value Of Cos Y Cos P 2 X Cos P 2 Y Cos X Sin Ycos P 2 X Cosxsin P 2 Y Is Zero If Brainly In




Solution Evaluate The Integral Of Sin 6 Xdx From 0 To P 2
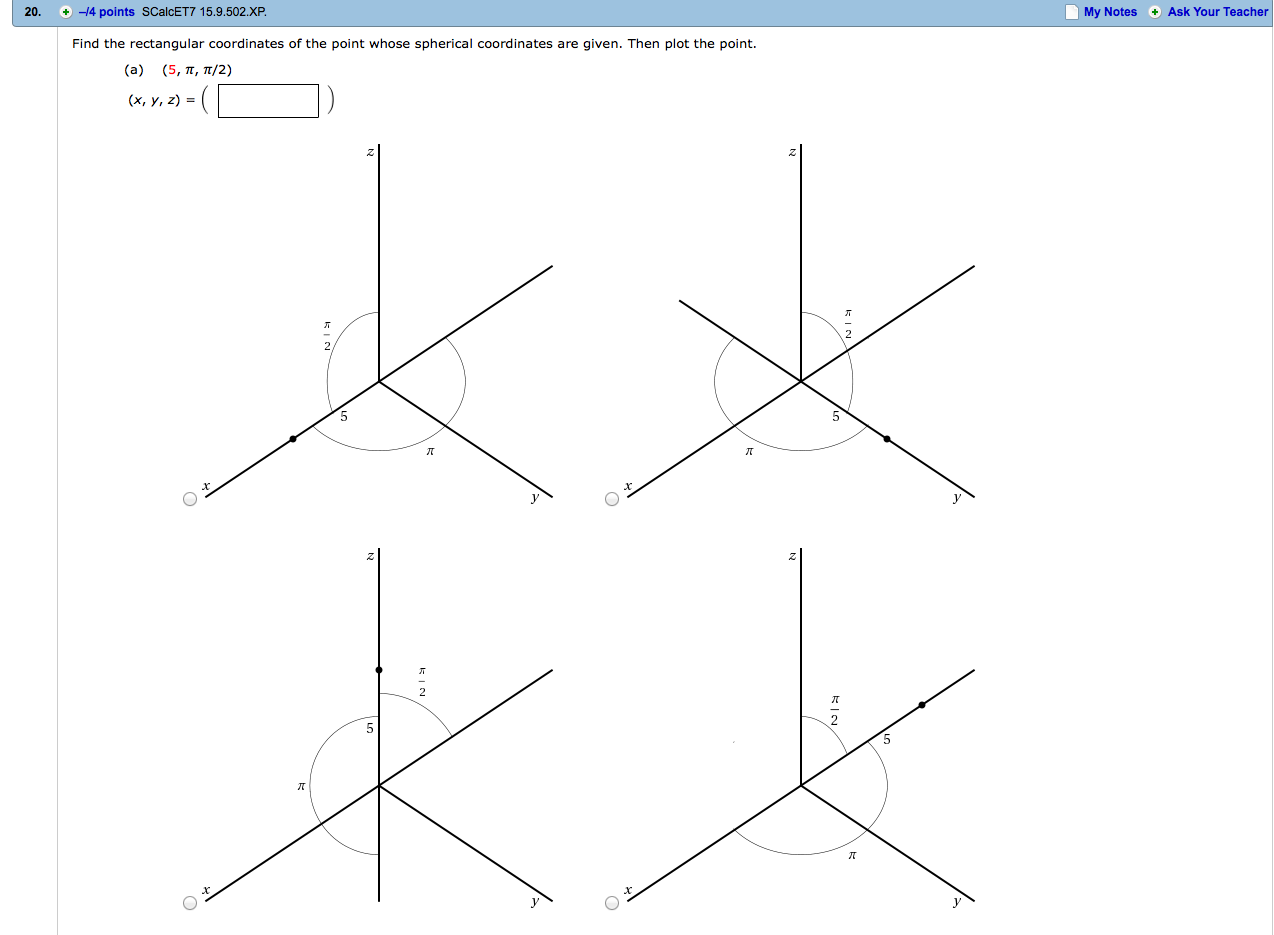



Find The Rectangular Coordinates Of The Point Whose Chegg Com



Welche Grenzwerte Existieren Mathelounge
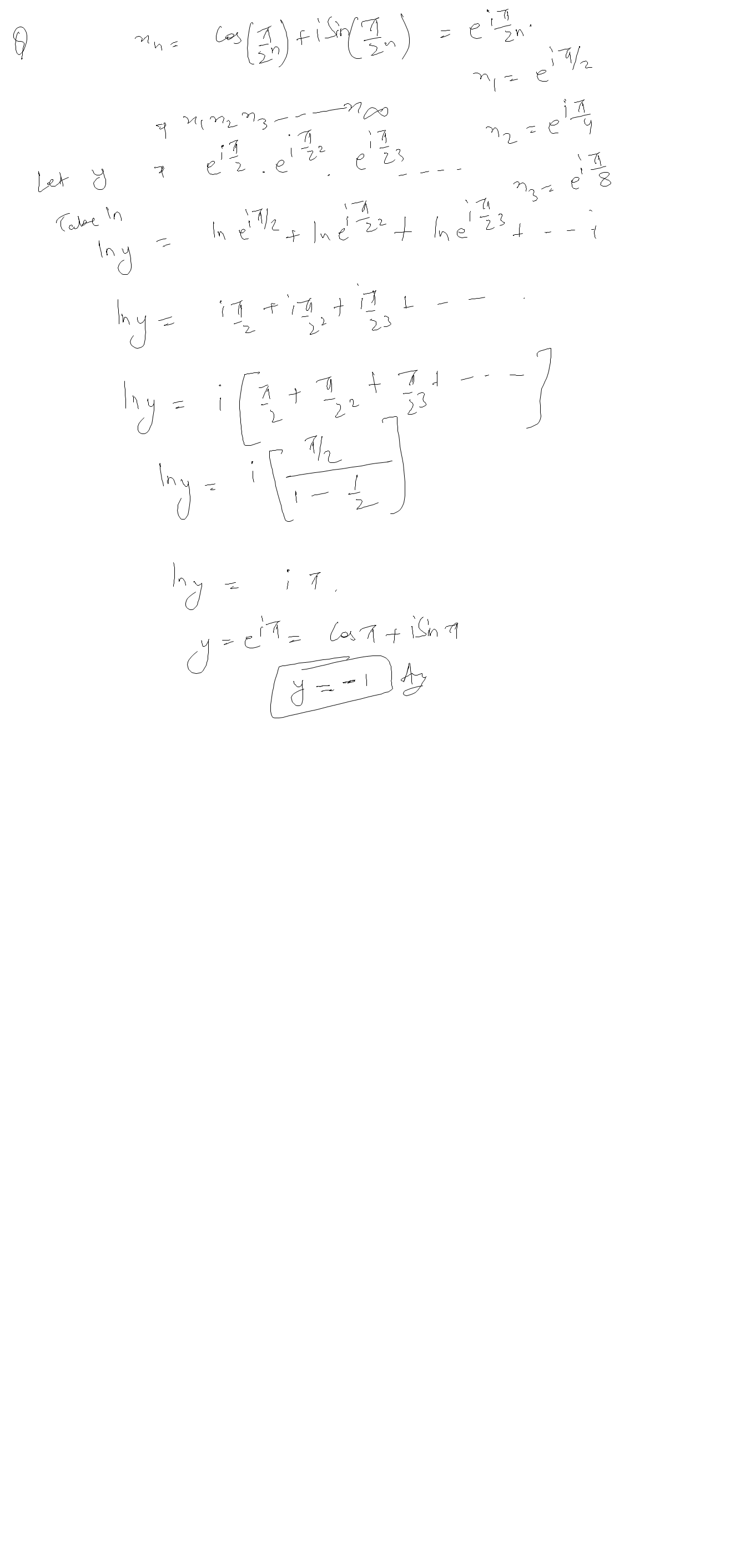



X N Cos P 2 N I Sin P 2 N N Is An Element Of N Then X 1 X Askiitians




Solve Sin 2x Cos 2x On The Interval X 0 2 P Gauthmath




P 2と P 3が どこから出てきたのか分かりません 教えてください ᯅ Clear




If Tan Pi 2 Theta 2 Sqrt 3 The Value Of Cos Theta Is Youtube



1



1




5 Ways To Calculate Pi Wikihow
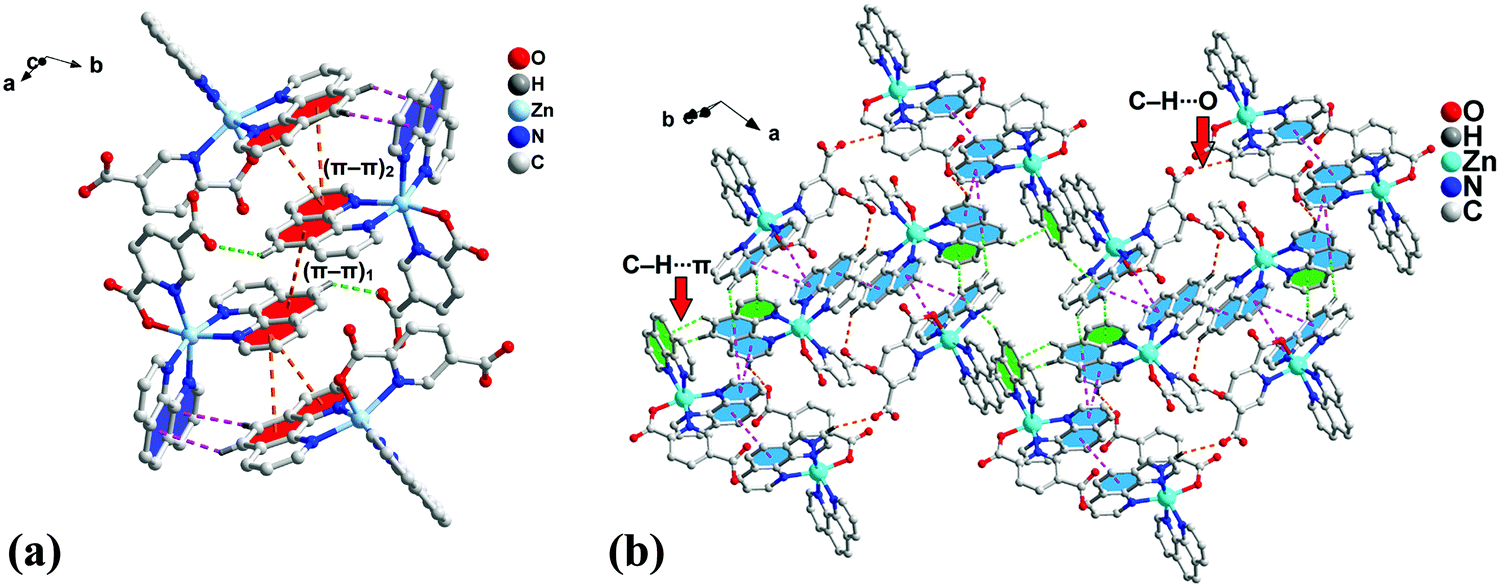



Biologically Relevant And Energetically Significant Cooperative Ternary P P 2 P P 1 P P 2 Assemblies And Fascinating Discrete H 2 O 21 Clust New Journal Of Chemistry Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D0nja




Prove That Dfrac Sin Pi X Cos Left Dfrac Pi 2 X Right Tan Left Dfrac 3pi 2 X Right Cot 2pi X Sin 2pi X Cos 2pi X Csc




Sin 4x Sin 2x X Frac P 2 Frac P 2 Gauthmath
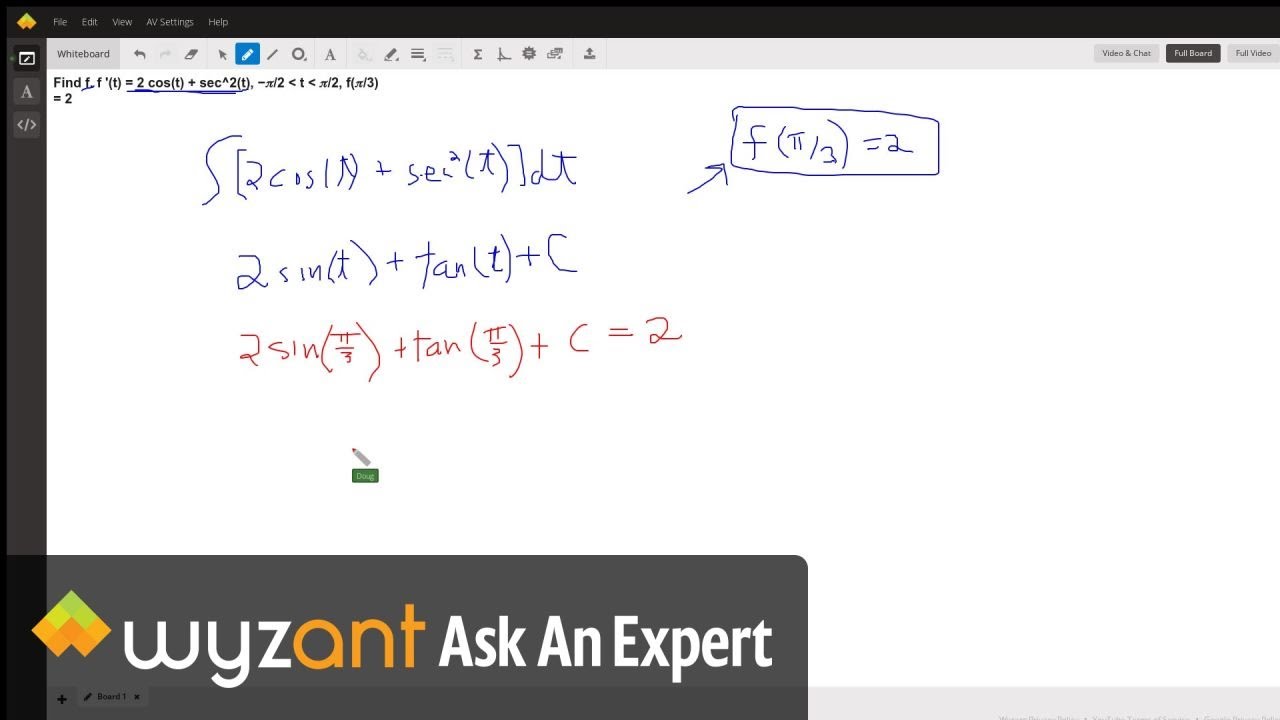



Find F F T 2 Cos T Sec 2 T 𝜋 2 T 𝜋 2 F 𝜋 3 2 Wyzant Ask An Expert




Inverse Trig Identity Arctan X Arccot X P 2 Peakd




Cos Pi 2
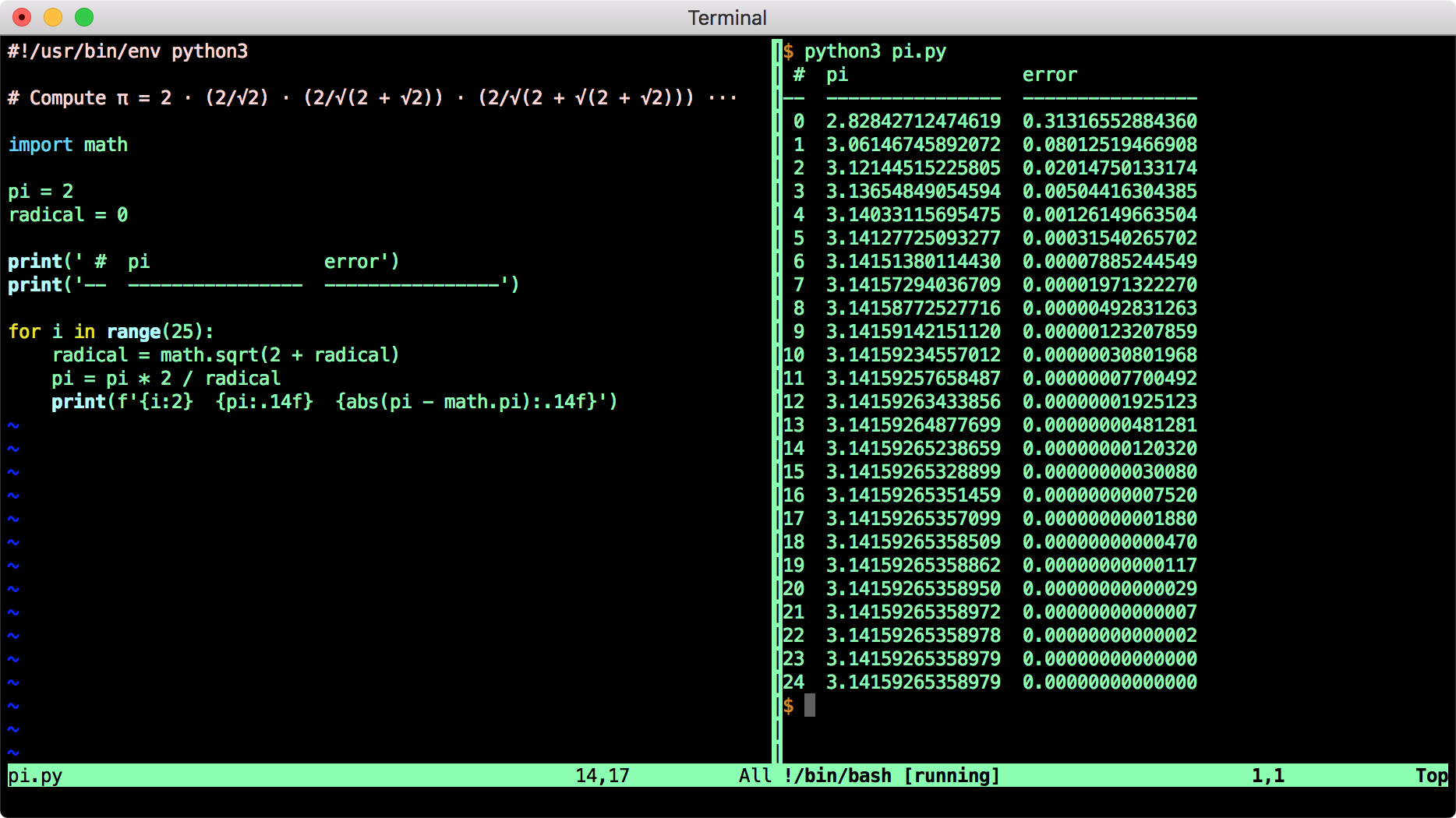



Susam Happy Pi Approximation Day P 22 7 22 July In Day Month Format Celebrate It By Baking An Approximation Of A Pie Or By Sharing Your Favourite P Representation Mine




A Formula For Sin Pi 2 N Mathematics Stack Exchange




Gpio Raspberry Pi Documentation




Evaluate The Following I Sin Pi 2 Sin 1 1 2 Ii Sin Pi 2 Sin 1 Sqrt3 2




The Integral Int Pi 2 Pi 2 E Sinx Cosx 1 E Tanx Dx




What S The Real Range Of Pitch And Roll Return By Sensormanager Getorientation Stack Overflow
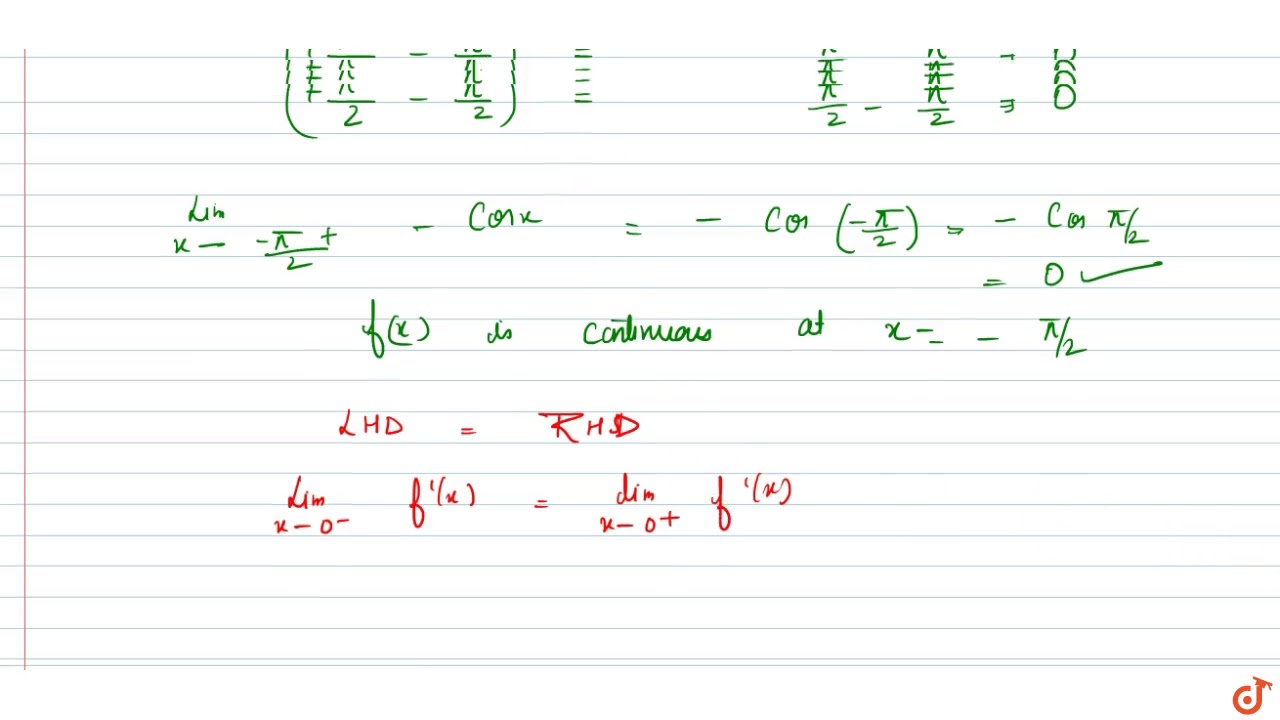



If F X X Pi 2 Xle Pi 2 And Cosx Pi 2 Lt Xle0 And X 1 0 Lt X Le1 And Lnx X Gt 1 Then Youtube




Given Sin A 8 17 And Cos A 0 Evaluate Si Nfra Gauthmath
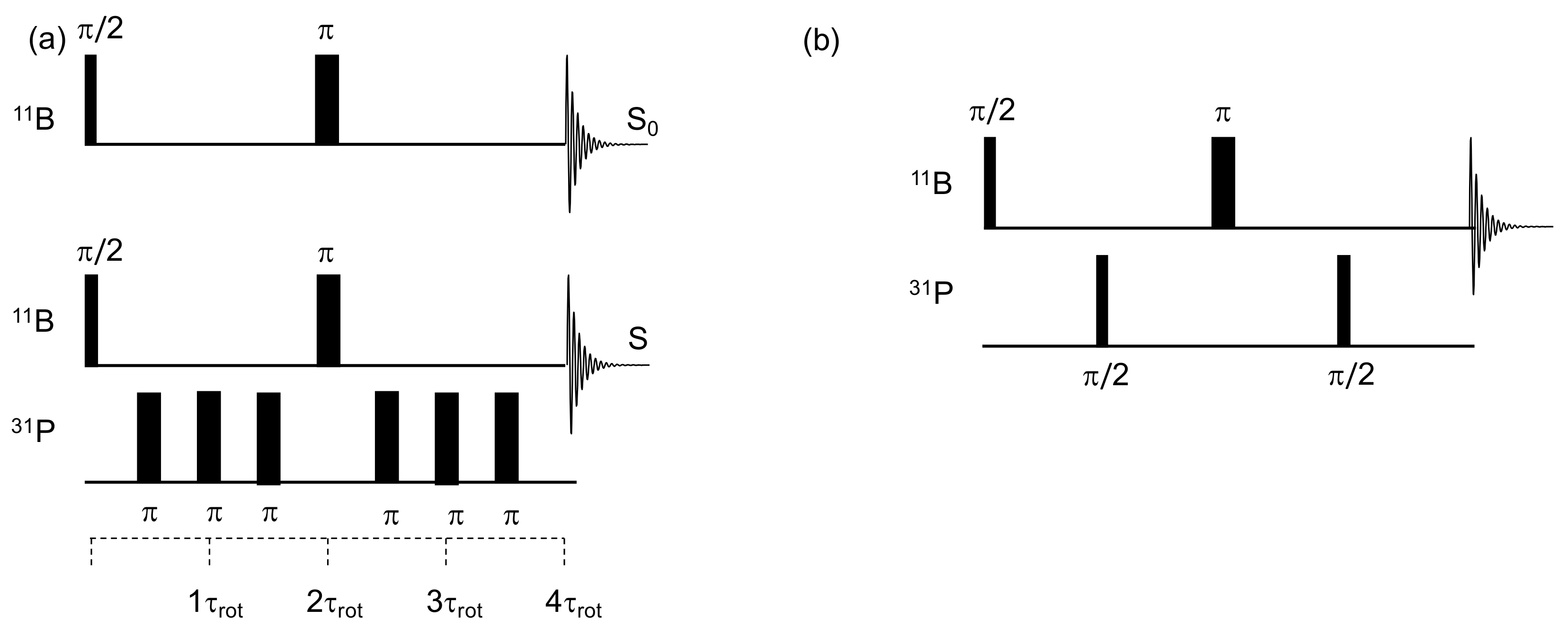



Molecules Free Full Text Solid State Nmr A Powerful Tool For The Characterization Of Borophosphate Glasses Html
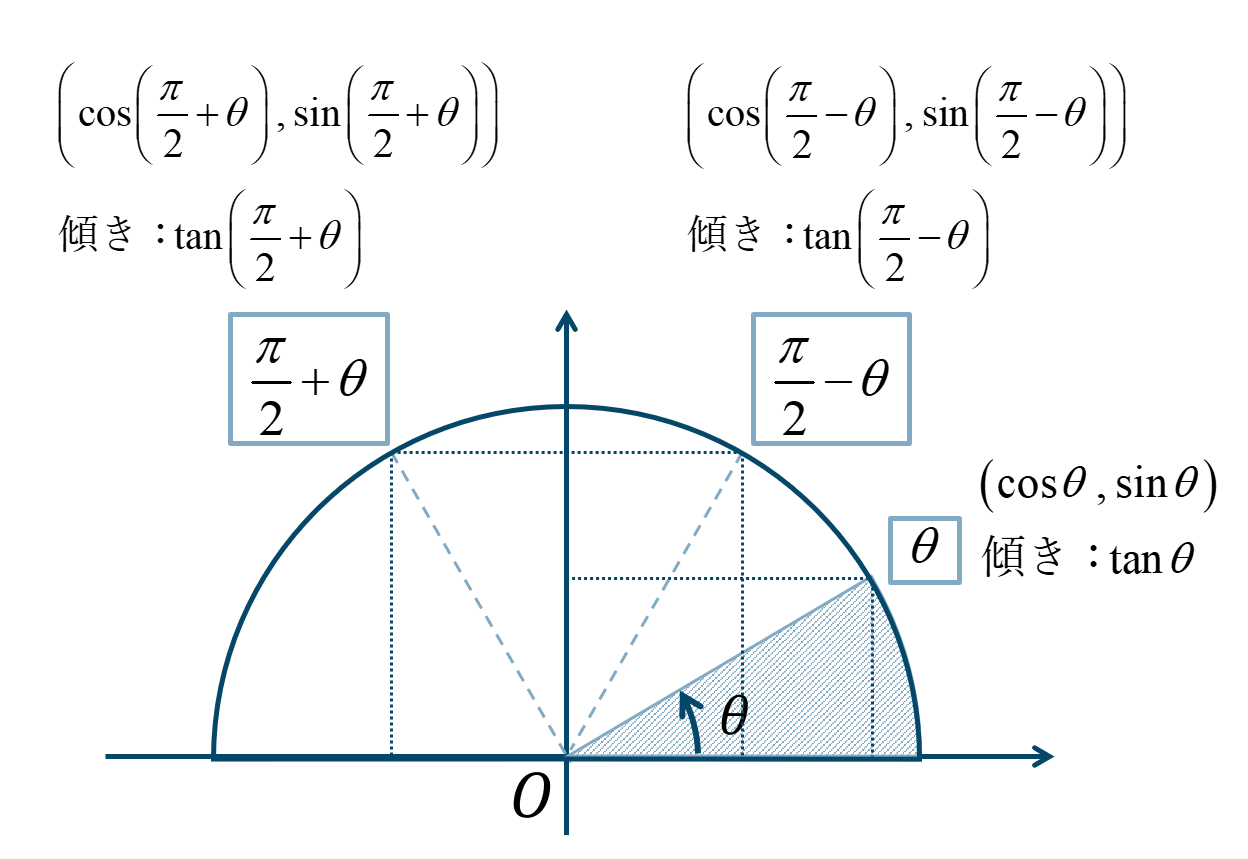



数学 P 2 8 P 2 8の三角関数の求め方とコツ ページ 2 教科書より詳しい高校数学



Asmr Mathematical Proof I I E P 2 2 Youtube



Cos P 2 万图壁纸网
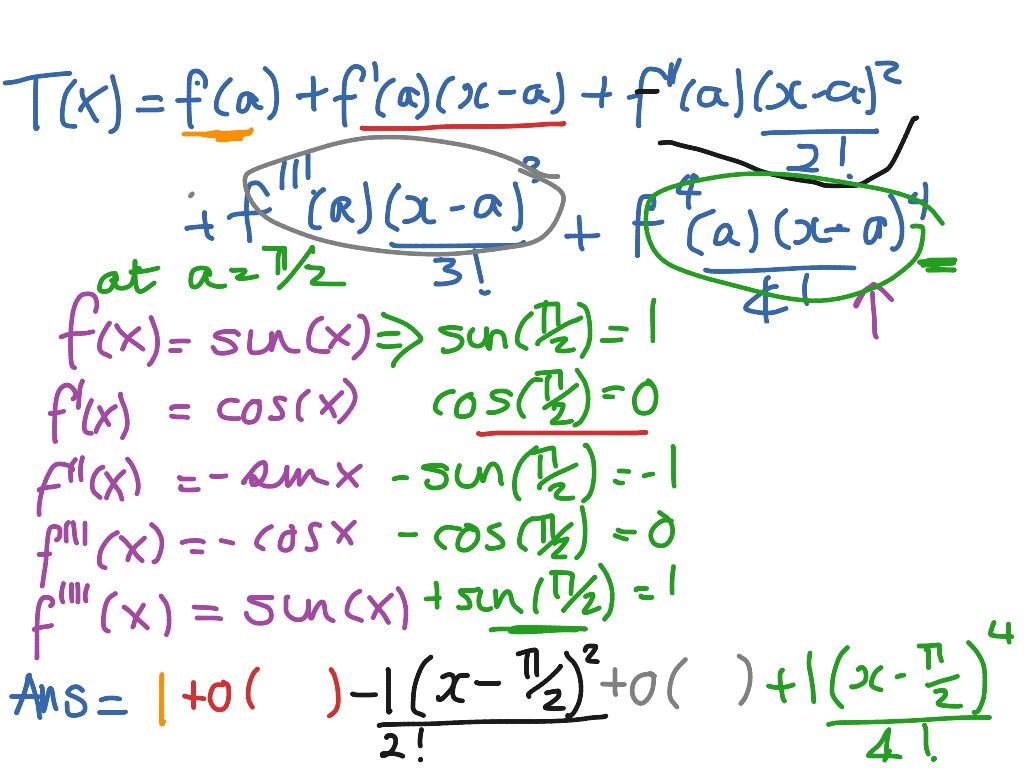



Taylor Series Of Sin X At Pi 2 Math Calculus Taylor Series Showme



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿